NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry InText Questions
These NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry InText Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry InText Questions
Try These (Page No. 67)
Question 1.
How will you construct a rectangle PQRS if you know only the lengths PQ and QR?
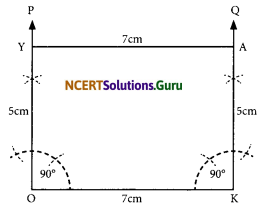
Solution:
A rectangle can be constructed by taking PQ as the length making an angle 90° at Q and cutting off QR, the breadth from the ray QY. The remaining two points R and S can be located by taking P and R as centres and radii as QR and PQ respectively to draw arcs to intersect at S. Thus, PQRS is the required rectangle.
![]()
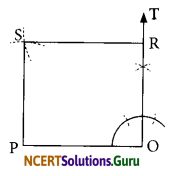
Question 2.
Construct the kite EASY if AY = 8 cm, EY = 4 cm and SY = 6 cm (Fig 4.26). Which properties of the kite did you use in the process?

Solution:
Following properties have been used in constructing the KITE:
(i) Diagonals are at right angles.
(ii) One of the diagonal bisects the other.
(iii) Pairs of consecutive sides are equal.
Steps of construction:
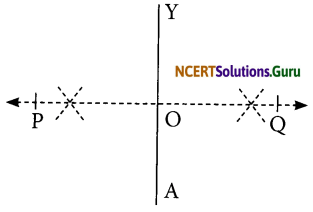
I. Draw a line segment AY = 8 cm.
II. Draw PQ, the perpendicular bisector of AY such that it meets AY at O.
III. We cannot locate a point E on PQ at 4 cm from Y and A, i.e., EY = 4 cm = EA is not possible.
IV. It is possible only when E and O coincide. In that case, the kite does not exist.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry InText Questions Read More »