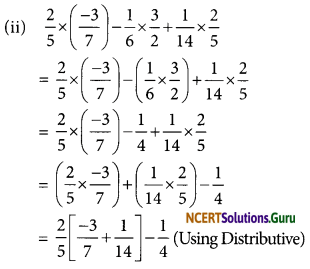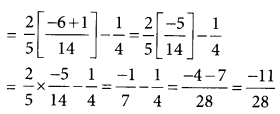These NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts to help students while preparing for their exams.
Stars and The Solar System NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17
Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
Page 234-235
Choose the correct answer in Questions 1-3.
Question 1.
Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
a. An asteroid
b. A satellite
c. A constellation
d. A comet
Answer:
c. A constellation
Question 2.
Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
a. Sirius
b. Mercury
c. Saturn
d. Earth
Answer:
a. Sirius
Question 3.
Phases of the moon occur because
a. we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us
b. our distance from the moon keeps changing
c. the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of moon’s surface
d. the thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant
Answer:
a. we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks:
a. The planet which is farthest from the Sun is ……………..
b. The planet which appears reddish in colour is ……………..
c. A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a ……………..
d. A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as ……………..
e. Shooting stars are actually not ……………..
f. Asteroids are found between the orbits of …………….. and ……………..
Answer:
a. Neptune,
b. Mars,
c. constellation,
d. satellite,
e. stars,
f. Mars and Jupiter
Question 5.
Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F):
a. Pole star is a member of the solar system. ( )
b. Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system. ( )
c. Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. ( )
d. INSAT is an artificial satellite. ( )
e. There are nine planets in the solar system. ( )
f. Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( )
Answer:
a. F
b. T
c. F
d. T
e. F
f. F

Question 6.
Match items in column A with one or more items in column B:

Answer:
i. (e) and (g),
ii. (a),
iii. (c) and (f),
iv. (d)
Question 7.
In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer:
The planet Venus is found in the western part of the sky after sunset and is known as an evening star.
Question 8.
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer:
Jupiter is the largest planet of the solar system.
Question 9.
What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer:
A group of stars which resembles certain shape is called a constellation. Great Bear and Orion are two examples of constellation.
Question 10.
Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in (a) Ursa Major and (b) Orion.
Answer:
(a) Ursa Major seems to be like a big ladle. There are four stars in the bowl of the ladle and three bright stars in the handle.
(b) Orion seems to be like a hunter. The three bright stars appear in the belt, while five bright stars are arranged in the form of a quadrilateral.

Question 11.
Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answer:
Apart from planets, asteroids and comets are also members of the solar system.

Question 12.
Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer:
Follow these steps for locating the pole star:
- Locate the Ursa Major and locate the quadrilateral in it.
- Select the two stars on the far side of the quadrilateral.
- Join these stars with a line and extend this imaginary line towards the top of the ladle.
- A faint star which meets this line is the Pole Star.

Question 13.
Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer:
All the stars move but their movement is not perceptible to us. Instead of that, it is the rotation of the Earth which creates an illusion of the movement of stars across the sky. But the pole star appears to be fixed at its position. This happens because the pole star is in line with the axis of rotation of the Earth.
Question 14.
Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years away from the Earth?
Answer:
The interstellar distances or intergalactic distances are too big to be easily expressed in terms of kilometres. Hence, we need a more convenient unit to express them. A light year is the distance travelled by light in one year. If a star is eight light years away from the Earth, it means that the light from that star takes eight years to reach us. This also means that the star which appears to our eyes is in fact the way it looked eight years ago.
Question 15.
The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer:
Earth and Jupiter can be considered as two spheres with radii R and R respectively. Given that the radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth.
Thus, R = 11 R
Volume of a sphere of radius r is given as = \(\frac {4}{3}\)πR3
Volume of the Earth = \(\frac {4}{3}\)πR3
And, volume of Jupiter =

Hence, this ratio suggests that Jupiter can accommodate 1331 Earths in it.
Question 16.
Boojho made the following sketch of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
Answer:

No, the diagram made by Boojho is not correct, because in the solar system the planets’ sequence on the basis of their distance from the Sun is like; Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The mistake he had done is that he changed the positions of the planets Venus, Mars, Neptune and Uranus. Besides this, he had shown in the diagram the Asteroids belt in the gap between the orbits of Saturn and Jupiter. This is incorrect. The Asteroids belt is located between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars. The correct diagram of the solar system is as follows:

NCERT Extended Learning Activities and Projects
Question 1.
The North-South line at your place: Let us learn to draw the north-south line with the help of the shadow of a stick. Fix a straight stick vertically in the ground where the Sun can be seen for most of the day. Call the foot of the stick as point O. Sometime in the morning, mark the tip of the shadow of the stick. Say this point is A. With OA as radius draw a circle on the ground. Wait till the shadow becomes shorter and then starts increasing in size. When the shadow again touches the circle, mark it as point B. Draw the bisector of the angle AOB. This is your North-South line. To decide which side of this line shows North, use a magnetic compass.

Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 2.
If possible, visit a planetarium. There are planetariums in many cities. In a planetarium you can see the motion of the stars, constellations and planets on a large dome.
Hint:
Do it yourself.

Question 3.
On a moonless night observe the sky for a few hours. Look out for a meteor, which appears as a streak of light. September-November is a good time for observing meteors.
Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 4.
Learn to identify the planets visible to the naked eye and some prominent constellations such as Great Bear (Saptarshi) and Orion. Also try to locate the Pole Star and the star Sirius.
Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 5.
Position of the rising Sun – Uttarayan and Dakshinayan:
This activity may last for several weeks. Choose a place from where eastern horizon is clearly visible. Choose also a marker, such as a tree or an electric pole, to mark the position of the rising Sun. It will be sufficient if you take the observation once every week. On any day, note down the direction of the rising Sun. Repeat this observation every week. What do you find? You would have noted that the point of sunrise changes continuously. From summer solstice (around 21 June), the point of sunrise gradually shifts towards the south. The Sun is then said to be in dakshinayan (moving south). It keeps doing so till winter solstice (around 22 December). Thereafter, the point of sunrise changes direction and starts moving towards north. The Sun is now said to be in uttarayan (moving north). From the equator, only on two days, on the days of the equinoxes (around 21 March and 23 September) the Sun rises in the east. On all other days, it rises either north of east or south of east. So, the direction of the rising Sun is not a good guide to determine directions. The Pole Star, which defines North, is a much better indicator of directions.
Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 6.
Form a group of students. Prepare a model of the solar system showing the planets, and their relative sizes. For this take a large chart paper. Make spheres representing different planets according to their relative size. You may use newspaper, clay or plasticine to make spheres. You can cover these spheres with paper of different colours. Exhibit your models in the class.
Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 7.
Try to make a scale model of the solar system showing distances of the planets from the Sun (Use Table 17.1 of NCERT Textbook). Did you face any difficulty? Explain it.
Hint:
Yes, the distance between the planets is so large that it becomes difficult to scale all of them to proper ratios. Moreover, there is a huge variation in the size of the planets and of the sun which becomes difficult to scale as some components may become very huge while the others become too tiny.

Question 8.
Solve the following riddle and try to make similar riddles yourself:
My first is in VAN but not in PAN
My second is in EARTH and also in HEAVEN
My third is in ONE and not in TWO
My fourth is in BUN and also in FUN
My last is in STAR but not in RADAR
I am a planet that moves round the Sun.
Hint:
Venus.
Activity 1
Objective: To show the position of the moon in its orbit and its corresponding phases. Materials Required: A big ball or a pitcher, white and black colour/paint.
Procedure:
- Take a big ball or a pitcher. Paint half of it white and half black.
- Go out into the playground with two of your friends. Draw a circle of radius of about 2 m on the ground. Divide the circle into eight equal parts as shown in the figure.

- Stand at the centre of the circle. Ask a friend to hold the ball at different points of the circle. Ask her to keep the white portion of the ball always towards the Sun. In each case, the line dividing the white and black portion is kept vertical.
- Standing at the centre of the circle, observe the visible white portion of the ball while your friend stands at the points on the circle marked earlier.
- Compare your observation with the different phases of the moon.
Observation: Following phases are observed: First quarter, waxing crescent, new moon, waning crescent, last quarter, waning gibbous, full moon, waxing gibbous. Conclusion: After the new moon day, the size of illuminated part of moon seen from Earth keeps increasing and after the full moon day it keeps on decreasing.
The Moon’s Surface: The moon’s surface is dusty, barren and has many different sizes craters on it. Moreover, there are many big and small mountains. The moon has no atmosphere and water.
Neil Armstrong was the first person to land on the moon followed by another astronaut Edwin Aldrin. Neil Armstrong landed on the moon on July 21, 1969.

Activity 2
Objective: To show that the moon completes only one rotation on its axis as it completes only one revolution around the Earth.
Procedure:
- Draw a circle of about 1 m diameter on the ground.
- Ask one of your friends to stand at the center of this circle.
- You revolve around your friend in such a manner that your face always remains towards him.
- Observe how many rotations did you complete in one revolution.
Observation: Your friend will not be able to see your back. You will complete only one rotation in one revolution.
Conclusion: The moon completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the Earth.
The Stars: A star is a huge celestial body having its own heat and tight. Stars produce heat and light because they are full of very hot gases. The Sun is the nearest star from us. It is at a distance of about 150,000,000 (one hundred fifty million) kilometres from us. The next nearest star from us is Alpha Centauri. This is about 40,000,000,000,000 (forty trillion) kilometres from us.
Light Year: The interstellar distances or intergalactic distances are too big to be easily expressed in terms of kilometres. Hence, we need a more convenient unit to express them. A light year is the distance travelled by light in one year. Distances of stars are usually expressed in terms of light years. The sunlight takes about 8 minutes to travel from the Sun to the Earth. This implies that the Sun is at a distance of 8 light minutes from us. Alpha Centauri is 4.3 light years away from us.
Pole Star: The pole star also called Polaris is situated close to the Earth’s axis of rotation. As a result, the position of the pole star appears to be fixed. This is unlike the other stars as their position keeps on changing with respect to the Earth.


Activity 3
Objective: To show that the pole star lies close to the axis of rotation of the Earth.
Materials Required: An umbrella and a white paper.
Procedure:
- Take an umbrella and open it.
- Make about 10-15 stars out of white paper.
- Paste one star at the position of the central rod of the umbrella and others at different places on the cloth near the end of each spike.
- Now, rotate the umbrella by rotating its central rod in your hand.
- Observe the stars on the umbrella. Observe if there is any star which does not appear to move.
Observation: The star situated at the central rod of the umbrella does not appear to move.

Conclusion: Pole star is the star which is situated in the direction of the Earth’s axis. It does not appear to move.
Constellation: The stars forming a group that has a recognisable shape is called a constellation. These constellations appear to move from east to west. The shape of all constellations seen in the sky always remains the same. Each constellation has been given the name of an animal or object, which it resembles.
Major Constellations
i. Great Bear: One of the most famous constellations which you can see during summer time, in the early part of the night is Ursa Major. It is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark. There are three stars in the handle of the ladle and four in its bowl. Ursa Major revolves around the pole star.
ii. Orion: Orion is also called the Hunter or Kalpurush. The three prominent stars in this constellation mark the belt of the hunter. An elaborate structure shows a man with a club and a shield. This constellation is visible in the southern sky, and this can be easily seen during summer months in India.

Sirius: The Sirius star is the brightest star of the sky. It can be located with the help of the Orion constellation. If we draw an imaginary line through the three stars in the middle of the Orion and extend further, we will reach the brightest star, Sirius.
iii. Cassiopeia: It is a constellation found in the Northern hemisphere and can be located in the sky during the winter season at the beginning of the night. The shape of this constellation resembles a W or a distorted M.
iv. Leo Major: It contains several bright stars making it one of the most easily recognisable constellations in the night sky. It is visible in both the northern and the southern hemispheres. In northern hemisphere, it can be seen from January to June.

The Solar System: The Sun and the celestial bodies which revolve around it forms the solar system. It consists of a large number of bodies such as the sun, planets, comets, asteroids and meteors.

The Sun: The Sun is the nearest star amongst all the stars present in the universe. It is the main source of heat and tight for all the planets specially Earth.
The Planets: Our solar system comprises eight planets namely Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn. Uranus and Neptune. The planets are like stars, but they do not have light of their own. They merely reflect the sunlight that falls on them. The planets keep changing their positions with respect to the stars. These are the objects revolving around the Sun in a fixed path. This fixed path is termed as an orbit.
Period of Revolution: It is the time taken by a planet to complete full revolution around the Sun.
Period of Rotation: It is the time taken by planet to complete one rotation around its own axis.
Activity 4
Objective: To show that planets move in their own orbits and they do not collide with one another.
Procedure:
- Go out into the playground with four or five of your friends.
- Draw fourcirclesofradii 1m, 1.8 m, 2.5 m and 3.8 m, all having a common centre.
- Ask one of your friends to stand in the center and represent the Sun. Your other four friends may represent Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
- Ask your friends to move around the Sun in anti-clockwise direction in their own orbits. Do they collide with one another?
Observation: They do not collide with one another, because they have fixed orbits of their own.

Conclusion: Planets moves in their own orbits so they do not collide.
Planets Revolving Around the Sun:
i. Mercury: It is the nearest planet to the Sun and the smallest planet present in our solar system. It is very difficult to observe it, as most of the time it is hidden in the glare of the Sun. It has no satellite of its own.
ii. Venus: It is the brightest planet. It is also called a morning or an evening star. It has no natural sateLlite of its own. Venus rotates from east to west, unlike the Earth which rotates from west to east. Venus also shows phases just like the moon.

iii. Earth: Earth is the only planet where life is known to exist. The Earth appears blue-green due to the reflection of light from water and landmass on its surface. The axis of rotation of the Earth is not perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. The tilt is responsible for the change of seasons on the Earth. It has only one satellite, the moon, of its own.

iv. Mars: It is called the red planet because it has a reddish colour. It has two moons of its own. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched India’s first Mars orbiter mission – Mangalyaan on November 5, 2013.

v. Jupiter: It is the largest planet of the solar system. It rotates very rapidly on its axis. Jupiter has a large number of satellites, and also has faint rings around it.
vi. Saturn: Saturn has thick rings around it that cannot be easily viewed with naked eyes. It has 30 natural satellites of its own. The density of Saturn is less than that of water making it the least dense planet of the solar system.

vii. Uranus: Just like Venus, Uranus rotates from east to west. It has 21 natural satellites. The rotation axis of Uranus is highly tilted. The atmosphere of Uranus mainly comprises hydrogen and methane gases.
viii. Neptune: It is the farthest planet from the Sun, hence, it takes the largest time to revolve around the Sun. It has 8 natural satellites of its own.

Satellites: These are the celestial bodies which orbit around other celestial body. Example: The moon is a satellite of the Earth.
Artificial satellites: These are the man-made satellites revolving around the Earth. These are launched from the Earth and revolve much closer to the Earth than its natural satellite, the moon. Aryabhatta was the first Indian satellite. Other examples are INSAT, IRS, Kalpana-1, etc. They are used for weather forecasting, transmitting radio
and television signals, telecommunication and remote sensing.

Asteroids: The smalt rock-like substances that are orbiting around the Sun are called asteroids. These are found in large gap between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter and form the asteroid belt. They are visible only through large telescopes.
Comets: Comets appear as a bright head with a long tail. They revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. The tail of a comet is always directed away from the Sun. The length of the tail grows in size as it approaches the sun.
Meteors: These are small objects that sometimes enter the Earth’s atmosphere. These occasionally enter the Earth’s atmosphere with very high speed. Due to friction of Earth’s atmosphere, these glow and then evaporate quickly. That is why the bright steak lasts for a very short time. However, meteors are large and so they can reach the Earth before they evaporate completely. Meteorites are the bodies that reach the Earth. Meteorites help scientists in investigating the nature of the material, from which the solar system was formed.

Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by celestial objects?
Answer:
Any naturally occurring object in the observable universe is called a celestial object. Stars, planets, satellites, comets, etc., are examples of celestial objects.
Question 2.
What is a light year?
Answer:
The distance travelled by light in one year is called a light year.
Question 3.
What is the solar system?
Answer:
The Sun, the eight planets, their moons and the other celestial objects that revolve around the Sun, form the solar system.

Question 4.
Why can’t we see the stars during the day?
Answer:
Due to the brightness of the Sun during the day, we cannot see the stars at that time.
Question 5.
If the planet Saturn is immersed in water, will it float or sink? Why?
Answer:
The planet Saturn will float because its density is less than that of water.
Question 6.
Define planets.
Answer:
Planets are heavenly bodies orbiting around the Sun. They look like stars but they do not have their own tight.
Question 7.
What is the direction of rotation of the Earth on its axis?
Answer:
West to east.
Question 8.
What is revolution?
Answer:
The movement of a celestial body in its orbit is called revolution.
Question 9.
What is rotation?
Answer:
The movement of a celestial body around its own axis is called rotation.

Question 10.
What is a satellite?
Answer:
A celestial body which moves around a planet is called a satellite.
Question 11.
Name the first Indian artificial satellite.
Answer:
Aryabhatta.
Question 12.
What are comets?
Answer:
A comet is a celestial body which revolves around the Sun in a highly elliptical path.
Question 13.
After how many years does Halley’s Comet appear from the Earth?
Answer:
76 years.
Question 14.
What is universe?
Answer:
The limitless expanse of space around us consisting of our solar system and the other stars and galaxies is called universe.
Question 15.
What are stars?
Answer:
The celestial bodies which have their own heat and light are called stars.
Question 16.
Name a star which lies stationary in the sky.
Answer:
Pole star.

Question 17.
Name the natural satellite of the Earth.
Answer:
Moon.
Question 18.
What is the distance of the Sun from the Earth? What is this distance called?
Answer:
The Sun is nearly 150,000,00 km away from Earth. The distance of Sun from Earth is 8.3 tight minutes and is called Astronomical Unit (AU).
Question 19.
Name the star which is nearest to the Earth after the Sun.
Answer:
Alpha Centauri.
Question 20.
Name some artificial satellites.
Answer:
INSAT, IRS, EDUSAT, Kalpana-1, etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write a short note on Pole Star.
Answer:
While other stars appear to move with gradual progress of night, the pole star remains fixed at its position. This happens because the pole star is in line with the axis of the Earth. The pole star appears in the northern sky. It is only visible from the northern hemisphere. However, the fixed position of the pole star has helped humans since ages.
Question 2.
What are asteroids?
Answer:
Asteroids are made up of rocks, metallic minerals and some ice. They are remnants of formation of the solar system. The asteroid belt is present between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This belt extends between 2.3 and 3.3 AU from the Sun.
Question 3.
Why is the Venus called the morning or the evening star?
Answer:
Venus is the brightest planet in the night sky. Venus is visible in early evening during the summer months and in early morning during winters. Due to this, Venus is also called the morning or evening star.

Question 4.
Why is the distance between the stars expressed in light years?
Answer:
Stars are very far from the Earth. Their distance, if written in kilometres, will not be convenient to read and memorise. Therefore, large distances are expressed in light year. It is the distance travelled by light in one year.
Question 5.
Why is Venus the hottest planet even though Mercury is closest to the Sun?
Answer:
Venus is a very hot planet (about 480°C), even hotter than Mercury, though it is further away from the Sun. This is because of the high percentage of carbon dioxide in its atmosphere, which causes heating due to the greenhouse effect.
Question 6.
How are stars different from planets?
Answer:
| Stars | Planets |
| 1. Emit their own light | 1. Do not emit their own light |
| 2. Made up of hot gases | 2. Made up of rocks |
| 3. When seen from the Earth, they twinkle | 3. Do not twinkle |
| 4. Massive in size | 4. Smaller than stars |
Question 7.
Differentiate between natural and artificial satellites.
Answer:
Natural satellites:
- Natural satellites are far away from the planets.
- They are comparatively larger in size and are present naturally.
- They do not have light of their own. They reflect the light from the Sun.
Artificial satellites:
- Artificial satellites are man-made and are sent from the Earth with specific requirements.
- Their distance, size and mass are lesser than the natural satellites.
- The electrical power required by artificial satellites is provided by panels of solar cells and small nuclear reactors.
Question 8.
Explain in brief about comets.
Answer:
Comets are small bodies which revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. They become visible from the Earth only when they come closer to the Sun. They are characterised by a small head followed by a long tail.
Question 9.
Why was Pluto out as a planet?
Answer:
In 2006, the international astronomical union adopted a new definition of a planet. According to this definition, a full fledged planet is an object that orbits the Sun and is large enough to have become round due to its own gravity.
In addition, the planet has to dominate the neighbourhood around its orbit. Pluto does not dominate its orbit as Charon, its large moon, is only half the size of Pluto, whereas all the true planets are far larger than their moons. Also, planets sweep up asteroids, comets, and other debris along their orbits while Pluto’s orbit is somewhat untidy. Hence, Pluto does not fit in the new definition of a planet and is no longer counted as a planet.

Question 10.
Why are meteors commonly called shooting stars?
Answer:
Meteors are smalt objects mainly made up of stones present in space. They regularly enter the Earth’s atmosphere. When a meteor enters the Earth’s atmosphere at high speed, it is heated by friction with air, and in most of the cases it burns to ashes in a very short time. As it heats up and burns, it appears as a glowing streak of light and is called a shooting star. Though it is called a shooting star, it is not a star at all.
Question 11.
What major factors have enabled life to evolve and survive on the Earth?
Answer:
All the factors necessary for life are present only on Earth. These are as follows:
- It has an atmosphere containing gases, like oxygen and carbon dioxide, which are necessary for survival.
- It has water in liquid form, which is essential for life.
- Being at the right distance from the Sun, it is not as hot as Mercury or Venus, nor is it as cold as the planets which are further away. This maintains a suitable temperature to support life.
Question 12.
Give five ways in which artificial satellites are useful to us.
Answer:
Artificial satellites are very useful to us in the following ways:
- They help in television and radio transmission.
- They help in telephone communication.
- They help us to study and forecast the weather by sending cloud pictures taken from the space to the Earth.
- They help in locating minerals.
- They help in studying agricultural yield on the Earth by photographing from above.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain some salient features of the Earth.
Answer:
Earth is the only planet where life is known to exist. According to scientists, earth is at a perfect distance from the sun and hence it has the right combination of gases, materials and temperature to support life. A major portion of the Earth’s surface is covered with water, and hence it appears blue from the space. Due to this, Earth is also called the blue planet.
Earth’s orbital plane is tilted at 23.5° on its equatorial plane. This means that Earth’s axis is tilted at 66.5° on its orbital plane. Seasons change on Earth because of this tilt.

Question 2.
Explain some common constellations in the night sky.
Answer:
A group of stars having a recognisable shape is called constellation. Constellation is an internationally defined area of celestial sphere. Some examples of constellations are described below:
a. Ursa Major can be seen in the sky during summer time in the early part of the night. It is also known as Big Dipper or Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big question mark or ladle.
b. Orion can be seen in the sky during winter in the late evenings. It has seven or eight stars. The brightest star Sirius is located close to the Orion.
c. Cassiopeia is a constellation that can be seen in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of night. It looks like distorted letter W or M.

Question 3.
What are planets? Describe all the planets in the solar system in brief.
Answer:
The bodies which revolve around the Sun in a certain orbit are called planets. There are eight planets in our solar system which are as follows:
- Mercury: It is the nearest planet to the Sun and is the smallest planet of our solar system. It is very close to the Sun so it is quite difficult to observe it. It has no satellite of its own.
- Venus: It is the Earth’s nearest planetary neighbour. It is the brightest planet in the night sky. Sometimes, it appears in the eastern sky before the sunrise, and sometimes in western sky just after the sunset. Thus, it is also called morning or evening star. It has no satellite of its own.
- Earth: It is the third planet. The Earth is the only planet in the solar system, on which life exists. Earth appears blue-green due to the reflection of light from water and landmass. It has only one moon.
- Mars: The fourth planet is called Mars. It is called the red planet. Mars has two small satellites.
- Jupiter: It is the largest planet of the solar system. It rotates very rapidly on its axis and has a large number of satellites. It also has a faint ring around it.
- Saturn: Saturn lies beyond Jupiter. It contains beautiful rings around it which are not visible with the naked eye. It has a large number of satellites. It is least dense among all planets; in fact its density is less than that of water.
- Uranus: It can be seen via telescope only. In its orbital motion, it appears to roll on its side. It rotates from west to east.
- Neptune: It can also be seen via telescope only. Neptune has a planetary ring system, though one much less substantial than that of Saturn.

Question 4.
What do you understand by phases of moon? What is the reason for the different phases of moon? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
The moon does not appear similar on all days, rather its shape changes every day. The different shapes of the moon are called the phases of moon.
Reason of Phases of Moon: The moon takes same time in completing a revolution and a rotation. Due to this, only one surface of the moon is visible from the Earth. The surface which is visible from the Earth gets varying ratios of light and shadow. Due to this, we are able to see different phases of the moon.

Picture-Based Questions
Question 1.
a. Draw a diagram to show the asteroid belt.
b. Name the planets between which the asteroid belt occurs.
Answer:
a.

b. Asteroid belt occurs between Mars and Jupiter.
Question 2.
Draw a diagram to show that moon is visible due to reflected sunlight, and answer the following questions:
a. How many moons does the Earth have?
b. Name a planet which has no moon.
Answer:

a. There is only one moon of the Earth.
b. Mercury is a planet which has no moon.



![]()
![]()