NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
These NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts to help students while preparing for their exams.
Microorganisms: Friend and Foe NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
a. Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a ………………
b. Blue green algae fix ……………… directly from air and enhance fertility of soil.
Alcohol is produced with the help of ………………
d. Cholera is caused by ………………
Answer:
a. microscope,
b. nitrogen,
c. yeast,
d. bacteria
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer:
a. Yeast is used in the production of
i. sugar
ii. alcohol
iii. hydrochloric acid
iv. oxygen
Answer:
ii. alcohol
b. The following is an antibiotic
i. Sodium bicarbonate
ii. Streptomycin
iii. Alcohol
iv. Yeast
Answer:
ii. Streptomycin
c. Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
i. female Anopheles mosquito
ii. cockroach
iii. housefly
iv. butterfly
Answer:
i. female Anopheles mosquito
d. The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
i. ant
ii. housefly
iii. dragonfly
iv. spider
Answer:
ii. housefly
e. The bread or idli dough rises because of
i. heat
ii. grinding
iii. growth of yeast cells
iv. kneading
Answer:
iii. growth of yeast cells
f. The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
i. nitrogen fixation
ii. moulding
iii. fermentation
iv. infection
Answer:
iii. fermentation
Question 3.
Match the organisms in Column A with their action in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Bacteria | (a) Fixing nitrogen |
| (ii) Rhizobium | (b) Setting of curd |
| (iii) Lactobacillus | (c) Baking of bread |
| (iv) Yeast | (d) Causing malaria |
| (v) A protozoan | (e) Causing cholera |
| (vi) A virus | (f) Causing AIDS |
Answer:
(i) → (e),
(ii) → (a),
(iii) → (b)
(iv) → (c)
(v) → (d),
(vi) → (f).
![]()
Question 4.
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Answer:
Microorganisms are too small so they cannot be seen with naked eye. They can be seen with the help of a magnifying glass or microscope. For example, fungus that grows on bread is so small that it can be seen only with the help of a magnifying glass or microscope.
Question 5.
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Answer:
The major groups of microorganisms are: bacteria, algae, fungi, protozoa and viruses.
- Bacteria: They are non-green single celled microbes. E.g., streptococcus.
- Fungi: They are long, thread like, unicellular as well as multicellular microorganisms. E.g., mushroom.
- Algae: Aquatic photosynthetic organisms commonly called seaweeds. E.g., Spirogyra.
- Protozoans: They are unicellular non-photosynthetic organisms. E.g., Amoeba.
- Viruses: They are non-cellular microbes which get activated only inside a living cell. E.g., EQV,
Question 6.
Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer:
Bacteria like Rhizobium, Azotobacter and blue-green algae can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Question 7.
Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Answer:
Usefulness of microorganisms:
- Lactobacillus helps in making curd from milk.
- Yeast helps in rising of dough and batter while making various food items.
- Yeast helps in fermentation and thus in production of wine.
- Antibiotics are made from microbes.
- Microbes help in cleaning the environment by decomposing dead remains of plants and animals.
- Microbes help in nitrogen fixation in the soil.
- Some microbes in our digestive system help in the digestion of food.
- Weak strains of some microbes are utilised to make vaccines against specific diseases.
- Microbes help in making of compost.
- Lactobacillus (present in curd) is beneficial for our health.
Question 8.
Write a short paragraph on the harmful effects of microorganisms.
Answer:
Micro-organisms cause diseases in animals. For example, in humans, bacteria cause diseases such as tuberculosis, cholera, typhoid, etc. In cattle, the foot and mouth disease is caused by a virus. Also, several microbes cause diseases in plants. For example, the productivity of wheat, orange, apple, etc., is reduced due to microbial diseases in plants. Certain microbes, on entering into our body, produce toxic substances. This leads to food poisoning. Some microorganisms, such as fungus, spoil our food. For example, bread, when left unused under moist conditions, gets spoilt by fungus which appears as a white cotton-like- growth on the bread.
![]()
Question 9.
What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Answer:
A substance which kills or stops the growth of bacteria is called antibiotic. Following precautions need to be taken while taking antibiotics:
- Never take an antibiotic without consulting a doctor.
- Always follow a doctor’s prescription while taking an antibiotic.
- Always complete the prescribed dose of antibiotic. Do not stop taking an antibiotic in between.
- Keep antibiotics away from children.
- Never use an antibiotic which is past its expiry date.
NCERT Extended Learning Activities and Projects
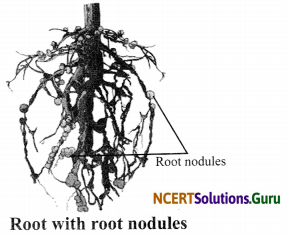
Question 1.
Pull out a gram or bean plant from the field. Observe its roots. You will find round structures called root nodules on the roots. Draw a diagram of the root and show the root nodules.
Hint:
The round structure are root nodules.
Question 2.
Collect the labels from the bottles of jams and jellies. Write down the list of contents printed on the labels.
Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 3.
Visit a doctor. Find out why antibiotics should not be overused. Prepare a short report.
Hint:
Antibiotics are powerful drugs that treat diseases caused by bacteria. Antibiotics kill and slow down the growth of bacteria in the body and further stop them from multiplying. However, overusing antibiotics can cause adverse effects.
- Due to overuse, certain bacteria grow their resistance power and thus the medicines do not work against them any longer.
- Other bacteria can also grow and cause infections.
- Overdose of antibiotics can also cause Diarrhoea and vomiting.
Thus it is essential to store and take medication correctly.
Question 4.
Project: Requirements – two test tubes, marker pen, sugar, yeast powder, two balloons and lime water. Take two test tubes and mark them A and B. Clamp these tubes in a stand and fill them with water leaving some space at the top. Put two spoonfuls of sugar in each of the test tubes. Add a spoonful of yeast in test tube B. Inflate the two balloons incompletely. Now tie the balloons on the mouths of each test tube. Keep them in a warm place, away from sunlight. Watch the set-up every day for next 3-4 days. Record your observations and think of an explanation.
Now take another test tube filled 1/4 with lime water. Remove the balloon from test tube B in such a manner that gas inside the balloon does not escape. Fit the balloon on the test tube and shake well. Observe and explain.
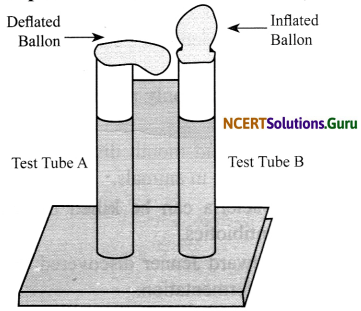
Hint:
The test tube B containing yeast shows inflated balloon due to formation of carbon dioxide gas by the yeast. Also, when carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky.
![]()
Activity 1
Objective: To prepare and study the temporary mount of bread mould.
Materials Required: A piece of bread, microscope, slide, coverslip, stain, a pair of forceps, water and bowl.
Procedure:
- Moisten a little piece of bread and put it in a bowl. Leave it undisturbed in a dark and cool place.
- After 4-5 days, prepare a slide of the mould growing on the bread.
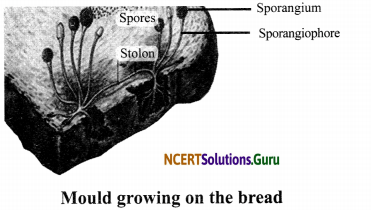
Observations:
- The mould growing on the bread is fungus.
- Spores are black or dark in colour.
- Sporangiophores bear sporangium that contain spores.
Conclusion: The bread mould is a fungus. Fungus depends on others for food. It is saprotrophic in nature.
iv. Protozoa: Protozoans are unicellular organisms. Protozoans do not have cell wall and chloroplast, but they do have nucleus. Protozoans are animal like just as algae are plant-like. Some are parasites that live in the bodies of other organisms, including human beings. Amoeba, Paramecium and Plasmodium are some examples of protozoa.

Viruses: Viruses are also microscopic but they are not considered as true living beings. They are considered as a borderline case between living and non-living. A virus behaves as a non-living thing when it is outside the host cell, i. e., a virus does not carry out nutrition, respiration or reproduction when it is outside the host. But once it is inside the host, it behaves like a living being, i. e., it carries out nutrition, respiration and reproduction. For example: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV), etc.
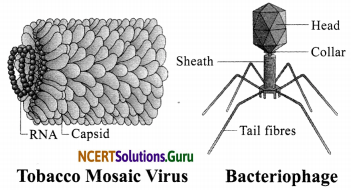
Friendly Microorganisms:
i. Lactobacillus is an example of a bacteria. Lactobacillus facilitates conversion of milk into curd.
Activity 2
Objective: To make curd.
Materials Required: Milk, teaspoonful of curd and a bowl.
Procedure:
- Heat some milk in a pan until it is lukewarm (40 – 45°C).
- Add a teaspoonful of pre-made curd to it and stir.
- Cover and leave it for 6-8 hours.
- The milk will get converted into curd.
Observation: When we add a teaspoonful of pre-made curd into a lukewarm milk, it gets converted into curd.
Conclusions: Milk is turned into curd with the help of a friendly bacteria (Lactobacillus), which was transferred to the milk as inoculum of curd.
ii. Yeast causes fermentation of many food items. The process by which sugar solution changes into alcohol due to anaerobic respiration by microbes is called fermentation.
iii. When yeast is added to batter of cake, idli or pakora, there is a production of carbon dioxide gas due to respiration by yeast cells. Carbon dioxide gas creates bubbles in dough or batter which makes fluffy cakes, breads, idli and dosa.
iv. Microorganisms are used in cleaning up of the environment as decomposers. For example, the organic wastes (vegetable peels, remains of animals, faeces, etc.) are broken down into harmless substances by bacteria.
v. In agricultural fields, microorganisms are used to increase soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
Commercial Use of Microorganisms:
- Microorganisms are used for large scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar). For commercial production of alcohol and wine, yeast is grown on natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice, crushed fruit juices, etc.
- Yeast is used commercially in the bakery industries for production of cakes, breads, etc.
![]()
Activity 3
Objective: To study the action of curd (or yeast) on the maida dough.
Materials Required: Maida, curd/yeast, a glass/stainless steel bowl.
Procedure:
- Take about 100 g of maida in a bowl, and mix it with a little warm water and about 30-40 g of curd or a little yeast.
- Knead it to a soft dough.
- Leave it at a warm place (around 35°C) for about 2-3 hours.
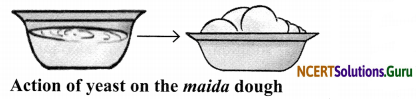
Observation: 2-3 hours later, the maida dough rises up and becomes fluffy.
Conclusion: When yeast/curd is added to the madia, there is a production of carbon dioxide gas due to respiration by yeast. Carbon dioxide gas creates bubbles in the dough or batter which makes the dough fluffy.
Antibiotic: Whenever we fall ill, the doctor may give us some antibiotic tablets, capsules or injections, like penicillin, which are made up of microorganisms. These are the medicines produced from bacteria and fungi used to kill or stop the growth of the disease causing microorganisms. Several antibiotics such as streptomycin, Chloromycetin, tetracycline, etc., are obtained from various fungi and bacteria. Antibiotics are used to cure a large number of diseases.
Antibody: When a disease causing microbe enter our body, our internal defensive mechanisms produce substances called antibodies in our blood to fight the disease causing microbe.
Vaccine: When a disease-carrying microbe enters our healthy body, the body produces antibodies which fights and kill these microbes. The body also remembers how to fight the microbe if it enters again. The antibodies remain in the body for a long time and protect us from the disease causing microbes. The substance which is injected into the body to trigger the body to initiate this entire process is called a vaccine. Vaccine contains dead or weakened pathogens which trigger the formation of suitable antibodies. These antibodies remain in the body and provide protection from the actual disease. The process of giving vaccine to people is known as vaccination. Edward Jenner discovered the first vaccine for smallpox in 1798. Vaccines are now available for many diseases like smallpox, tuberculosis, polio, tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough, hepatitis, etc.
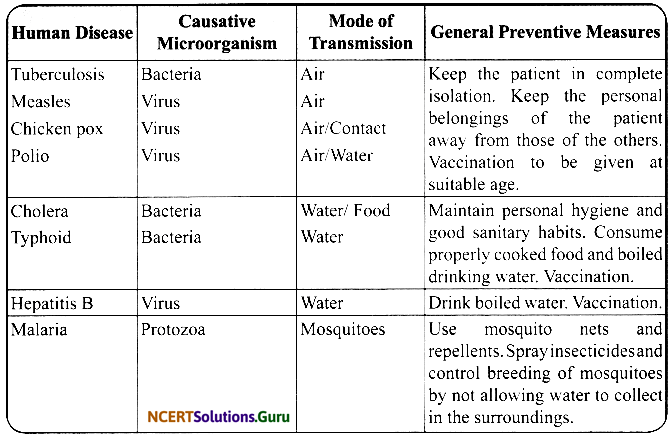
Harmful Microorganisms: A microbe which causes disease is called a pathogen. Diseases caused by pathogens can be broadly grouped into two categories:
i. Communicable Disease: The disease which can spread from one person to another is called a communicable disease. Some insects and animals that carry such pathogens from one body to another are called carriers or vectors, for example, housefly.
ii. Non-communicable Disease: The disease cannot spread from one person to another are called non-communicable diseases. Some common pathogens and diseases caused by them in animals and humans are listed below:
Microbes also cause diseases in animals, such as anthrax disease in cattle is caused by bacterium Bacillus anthracis, and in plants, like citrus canker which is caused by bacteria in citrus fruits. Other plant diseases include rust of wheat (caused by a fungus) and yellow vein mosaic of okra (caused by a virus).
Pathogen | Disease | Mode of Transmission |
| Plasmodium | Malaria | Spreads through the bite of female Anopheles mosquito |
| Dengue virus | Dengue | Spreads through the bite of female Aedes mosquito |
| Common cold virus | Common cold | Through air, when someone coughs or sneezes |
| Many bacteria | Cholera, diarrhoea | Through contaminated food and water |
| Flepatitis B vims | Hepatitis B | Through exchange of body fluids |
| HIV | AIDS | Through exchange of body fluids |
| Bacillus anthracis | Anthrax (in animals) | Through contact |
Food Poisoning: Some bacteria produce toxic substances in food. Consuming a food item with toxic substance can result in food poisoning. Food poisoning is a serious case and needs immediate hospitalisation. Lack of timely care in case of food poisoning may prove fatal.
Food Preservation: The process by which spoilage of perishable food is prevented using chemical or physical methods is called food preservation. We know that microbes proliferate very fast in the presence of food, Common preservatives used are common salt, sugar, edible oils, vinegar, sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite. Boiling and storing the things at low temperature also help in preserving food items. Dry fruits and even vegetables are sold in sealed air-tight packets to prevent the attack of microbes.
Pasteurisation: It is the process in which milk is heated at about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then swiftly chilled and stored. This process prevents the growth of microbes. This process was conceptualised by Louis Pasteur in 1857 therefore, it is known as pasteurisation.
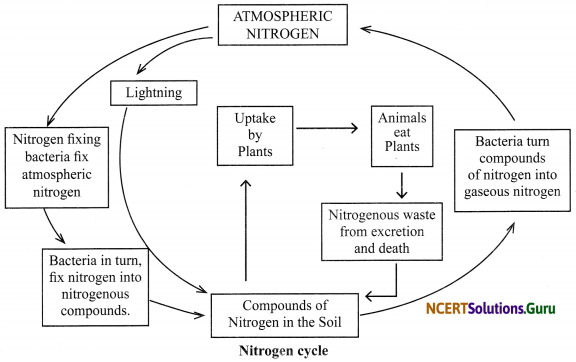
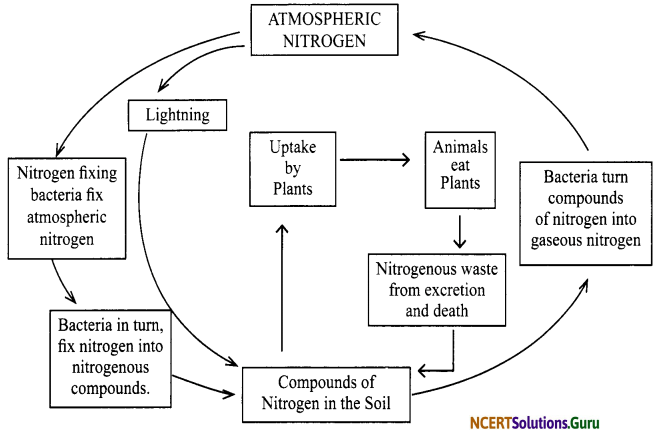
Nitrogen Fixation: The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites which can be taken up and used by plants to make the required molecules is known as fixing of nitrogen.
Nitrogen cycle: The circulation of nitrogen through living things (plants and animals) and non-living environment (air, soil and water) is called nitrogen cycle in nature. Some bacteria and blue green algae, present in the soil, fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into nitrogenous compounds. Once nitrogen is converted into these usable compounds, it can be utilised by plants from the soil through their root system. On the other hand, when plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi present in the soil convert the nitrogenous wastes into nitrogenous compounds to be used by the plants again. Nitrogen gas is also released to the atmosphere during this process. Due to this nitrogen cycle, the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains more or less constant.
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are microorganisms?
Answer:
Organisms which cannot be seen by naked eyes are called microorganisms or microbes.
Question 2.
Name two habitats of microorganisms.
Answer:
Soil and water.
Question 3.
What are viruses?
Answer:
Very tiny microscopic organisms which reproduce only inside the cells of the host organisms are called viruses.
Question 4.
Name some diseases caused by Protozoans.
Answer:
Dysentery and malaria.
![]()
Question 5.
Mention two groups of microorganisms which live in colonies.
Answer:
Bacteria and fungi.
Question 6.
Mention some diseases caused by bacteria.
Answer:
Typhoid and tuberculosis (TB) are bacterial diseases.
Question 7.
Name the most popular vaccination programme.
Answer:
Pulse polio programme.
Question 8.
What is polio?
Answer:
Polio is a disease which affects nerves and results in paralysis, especially of legs.
Question 9.
What is a communicable disease? Give examples.
Answer:
A disease which can spread from one person to another is called a communicable disease. Example: cholera and chickenpox.
Question 10.
What do you mean by antibodies?
Answer:
Antibodies are the substance released by the immune system of the body to fight off and kill the disease causing pathogens that enter our bodies.
Question 11.
What is a vaccine?
Answer:
A preparation containing usually killed or weakened microorganisms that is given to a person to provide protection against a particular disease is called a vaccine.
Question 12.
What do you mean by vaccination?
Answer:
The process of administering a vaccine in the body of an individual is called vaccination.
![]()
Question 13.
What are the carriers of diseases- causing microbes.
Answer:
The insects and animals which help in the transmission of the pathogens from source to a healthy person are called carriers of disease-causing microbes.
Question 14.
Name the carrier of dengue virus.
Answer:
Female Aedes mosquito.
Question 15.
What is nitrogen fixation?
Answer:
The process of changing atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds of nitrogen which can be taken up by plants is called nitrogen fixation.
Question 16.
Name the pathogen of anthrax.
Answer:
Bacillus anthracis.
Question 17.
What do you mean by symbiotic relationship?
Answer:
The relationship between two organisms in which both the organisms are benefitted is called a symbiotic relationship. For example, association of fungi and algae in lichens.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the main characteristics of viruses?
Answer:
The main characteristics of viruses are:
- They have no cell wall.
- They cause various diseases like eye flu.
- They multiply only in the host body.
- Antibiotics do not affect them.
![]()
Question 2.
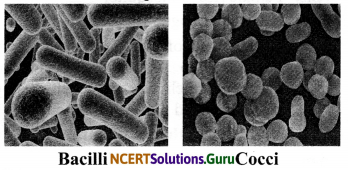
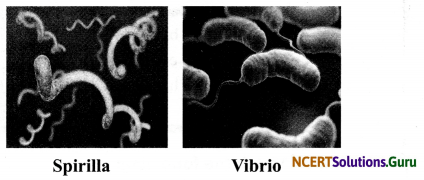
Describe the different types of bacteria on the basis of their shape giving examples.
Answer:
a. Bacilli: Bacilli are rod-shaped bacteria that look like cylinders, arranged singly or in chains. For example, Lactobacillus.
b. Cocci: Cocci are round, spherical-shaped bacteria. They can occur as a single bacterium or can be arranged in pairs. For example, Staphylococcus.
c. Spirilla: These are twisted spiral-shaped bacteria that look like a ribbon such as Spirillum.
d. Vibrio: These are comma-shaped bacteria which look like a bent rod. For example, Vibrio cholerae.
Question 3.
Describe the discovery of Penicillin.
Answer:
Alexander Flemming, a British scientist, was the first to discover that Penicillium mould produces an antibiotic called penicillin. He detected penicillin just by chance, when he observed that Penicillium grown in his culture of bacteria (staphylococcus), prevented the growth of bacteria in the culture. Now several antibiotics such as streptomycin, Chloromycetin, tetracycline, etc., are obtained from various fungi and bacteria.
Question 4.
Why do antibiotics have no effect on viruses?
Answer:
Antibiotics have no effect on viruses because viruses do not have a metabolism of their own. The antibiotics act by hampering the metabolism of the microorganisms rendering them harmless or killing them. Since the viruses have no metabolism of their own and they rely on the host enzymes and machinery, thus antibiotics have no effect on them.
Question 5.
How do the microorganisms survive under adverse conditions?
Answer:
Under unfavourable conditions of temperature, water and availability of food, microorganisms generally form a hard and tough covering called cyst or spore. This covering protects them from the harsh conditions. The covering is shed away when favourable conditions reappear.
Question 6.
What is the role of yeast in baking industry?
Answer:
Yeast plays an important role in the baking industry. Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of the gas fill the dough and increase its volume. Thus, they are helpful in baking industry and make the stuffs soft, spongy and fluffy.
![]()
Question 7.
How does a vaccine work?
Answer:
When a vaccine is inoculated in the body of an individual, the body prepares antibodies against it. Thus, the body learns and remembers how to fight with that particular microbe in future. In this way, vaccination helps in prevention against a particular disease.
Question 8.
Describe the role of blue-green algae and bacteria in enhancing the fertility of soil.
Answer:
Some bacteria and blue green algae fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and enrich soil with nitrogen, thereby increasing its fertility. These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers. Thus, bacteria and blue green algae increase the soil fertility. For example, Rhizobium, Azotobactor and Clostridium.
Question 9.
How do the microbes help in cleaning the environment?
Answer:
Many microbes feed on dead remains of plants and animals. These microbes play the role of decomposers. Thus, microbes help in clearing organic waste from our surroundings. Dead cattle, waste from meat and fish shop, waste from vegetable market, etc., are decomposed and cleaned away by the action of microbes.
Question 10.
How do microorganisms spoil food?
Answer:
Microorganisms grow on the food materials and multiply rapidly. They release toxins in the food and make it unfit for consumption. They breakdown the food molecules into amines and change the taste, texture and appearance of food. This results in food poisoning.
Question 11.
What do you understand by pasteurisation?
Answer:
Pasteurisation involves heating the milk to 70°C for about 15 to 30 minutes and it is then quickly cooled down and stored. It helps in killing the microbes which may be present in the milk. It is a method of food preservation. Milk is pasteurised before being packed.
Question 12.
Differentiate between yeasts and moulds.
Answer:
| Yeasts | Moulds |
| 1. They are unicellular. | 1. They are multicellular. |
| 2. Reproduce by budding. | 2. Reproduce by spores. |
| 3. Yeasts are both aerobic and V anaerobic. | 3. Moulds are aerobic. |
Question 13.
Suggest three methods to prevent the growth of moulds.
Answer:
Methods to prevent the growth of moulds are as follows:
- Storing the things at low temperatures and in clean, closed containers.
- Keeping the things in dry conditions or in dry storage.
- Sun Drying: This is a traditional c. Using preservatives for storing the food.
- Keeping the articles away from the reach of microorganisms present in the air.
![]()
Question 14.
Suman bought some mangoes from a market. She could not eat them for a few days. After a few days, she found that they were spoilt and rotten. But she knows that the mango pickle her mother makes does not spoil for a long time. Her mother told her that bacteria are responsible for the spoilage of fruits.
a. Why did mangoes get spoilt?
b. Give the names of any four fruits and vegetables which are preserved in salt and sugar.
Answer:
a. Mangoes get spoiled because they have much higher moisture content (water content) which promotes the growth of food spoiling microorganisms.
b. Raw mango, amla, carrot, beans.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are food preservatives? Explain some common methods of food preservation.
Answer:
Some common chemicals generally used to check the growth of microbes are called food preservatives. We know that microbes proliferate very fast in presence of food, moisture, oxygen and ambient temperature. All the methods of food preservation are aimed at ruling out the food, moisture, oxygen and ambient temperature for microbes so that they won’t proliferate. Some common methods of food preservation are as follows:
a. Sun drying: This is a traditional method of food preservation. Sun-drying helps in removing moisture from the food. Grains are dried in the Sun before being stored. Many vegetables are also Sun-dried so that they can be used in off-season.
b. Preservation by Common Salt: When a food item is kept in plenty of salt, water from the food comes out because of osmosis. It results in dehydration of the food item. Absence of moisture helps to prevent the growth of microbes. Fish, meat and pickles are preserved by adding salt.
c. Preservation by Sugar: Sugar preserves food by reducing moisture in it. Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by adding sugar.
d. Preservation by Oil and Vinegar: The layer of oil on the top of food prevents oxygen from entering the food. Some microbes do not survive in the absence of oxygen. Some microbes cannot survive in acidic environment and thus vinegar is an effective food preservative.
e. Storage and Packing: Some food items are stored in air-tight packets so that oxygen is not available for proliferation of microbes. Some food items are packed in cans, along with some preservatives. Oily food, such as potato chips, is packed in air-tight packets which are filled with nitrogen gas. Nitrogen gas prevents the oily food from becoming rancid.
f. Boiling and freezing: Boiling kills many microbes. Similarly, we keep our food in refrigerator. Low temperature inhibits the growth of microbes. Meat, fish, fruits, etc., need extensive freezing and sterilisation facilities for storage.
Question 2.
Mention the places where the following microorganisms are found:
a. Bacteria
b. Protozoa
c. Fungi
d. Algae
e. Viruses.
Answer:
a. Bacteria: They are found almost everywhere especially in soil, hot springs and organic matter.
b. Protozoa: They are found mostly in soil and fresh and marine water. Some are found in living organisms and cause diseases like malaria.
c. Fungi: They are mostly found in warm and humid places. They are also found on decaying organic matter such as food, fallen logs, etc.
d. Algae: They are often present in ponds. Some algae are found in snow and some in hot springs. They also grow in moist soil, on barks of trees and on rock surfaces.
e. Viruses: Viruses inhabit and reproduce only inside the cells of living organisms such as plants, animals and human beings.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the uses of bacteria, fungi and algae.
Answer:
a. Uses of Bacteria:
- They are used to increase the soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
- Some bacteria are used to produce antibiotics.
- Some bacteria help in many functions of our body.
- Lactobacillus bacterium converts milk into curd. It also helps in the digestion of food.
b. Uses of Fungi:
- Yeast is used to prepare alcohol and vinegar by fermentation.
- Yeast is used to produce breads, cheese, bear, wine, etc.
- Mushrooms are eaten as food.
- Yeast is used to produce vitamin B.
- Penicillin is an antibiotic formed from a fungus called Penicillium.
c. Uses of Algae:
- Algae are used to make jellies.
- They are used in soups, ice creams, jellies and jams as thickening agent.
- Chlorella is used to produce vitamin B.
- Silica from diatoms is used in toothpastes.
Question 4.
Explain the nitrogen cycle in nature.
Answer:
Our atmosphere has 78% nitrogen gas. The atmospheric nitrogen cannot be taken up directly by plants and animals. Certain bacteria and blue- green algae present in the soil fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into compounds of nitrogen. Once nitrogen is converted into these usable compounds, it can be utilised by plants from the soil through their root system. Nitrogen is then used for the synthesis of plant proteins and other compounds. Animals feeding on plants get these proteins and other nitrogenous compounds. When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi present in the soil convert their nitrogenous wastes into nitrogenous compounds to be used by the plants again. Certain other bacteria convert some part of them back to the nitrogen gas which goes back into the atmosphere. As a result, the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains more or less constant.
Question 5.
Explain some indications which help to detect the spoilage of food.
Answer:
Following indications help us in detecting the spoilage of food:
- Odour: When food gives out bad smell, it is the indication that the bacteria have spoiled the food.
- Discolouration: Growth of microbes on food results in discolouration of food e.g., black moulds on breads.
- Souring: Sometimes the cooked food starts tasting sour. It is due to the production of acids by the action of certain bacteria.
- Sliminess: Sometimes the food becomes slimy. It is also due to action of certain bacteria.
- Gas formation: Due to action of bacteria gases, like carbon dioxide are produced. They also spoil the food by making it spongy or swollen.
![]()
Question 6.
Make a table of common human diseases caused by microbes.
Answer:
Picture-Based Questions
Question 1.
a. Draw a diagram to show any two algae and name them.
b. Draw a diagram to show any two protozoa and name them.
Answer:
a. Algae – Chlamydomonas and Spirogyra.

b. Protozoa – Amoeba and Paramecium.

Question 2.
a. Draw a diagram of: (i) Bread mould, (ii) Penicillium and (iii) Aspergillus.
b. Name the group to which the above microorganisms belong.
Answer:
a.

b. Above microorganisms belong to the fungi group.
![]()
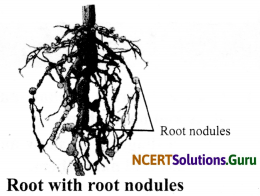
Question 3.
Draw a diagram of roots of leguminous plant with root nodules. Name the bacteria that live in these roots.
Answer:
The bacteria that live in these roots are Rhizobium bacteria
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Read More »






























