MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 MCQ Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Graphically, the pair of equations
6x – 3y + 10 = 0
2x-y + 9 = 0
represents two lines which are
(A) intersecting at exactly one point
(B) intersecting at exactly two points
(C) coincident
(D) parallel
Answer:
(D) parallel
Explanation:
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{6}{2}=3\) \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}=\frac{-3}{-1}=3\) \(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=\frac{10}{9}\)
⇒ \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
So, the system of linear equations is inconsistent (no solution) and graph will be a pair of parallel lines.
![]()
Question 2.
The pair of equations x + 2y + 5 = 0 and -3x -6y + 1 = 0 have:
(A) a unique solution
(B) exactly two solutions
(C) infinitely many solutions
(D) no solution
Answer:
(D) no solution
Explanation:
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{1}{-3}\)\(=-\frac{1}{3},\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}{a}\)\(\frac{-1}{3},\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}=\frac{5}{1}\)
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
So, the system of linear equations has no solution
Question 3.
If a pair of linear equations is consistent, then the lines will be: ‘
(A) parallel
(B) always coincident
(C) intersecting or coincident
(D) always intersecting E
Answer:
(C) intersecting or coincident
Explanation:
Condition for consistency:
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}} \neq \frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\)has unique solution (consistent), i..e.,
intersecting at one point
\(\text { or } \frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}=\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
(Consistent lines, coincident or dependent)
Question 4.
The pair of equations x = a and y = b graphically represents lines which are :
(A) parallel
(B) intersecting at (b, a)
(C) coincident
(D) intersecting at (a, b)
Answer:
(D) intersecting at (a, b)
Explanation:
(x= a) is the equation of a straight line parallel to the y-axis at a distance ‘a’ from it. Again, y = b is the equation of a straight line parallel to the x-axis at a distance b from it. So, the pair of equations x = a and y = b graphically represents lines which are intersecting at (a,b).
![]()
Question 5.
The pair of equations y = 0 and y = – 7 has :
(A) one solution
(B) two solutions
(C) infinitely many solutions
(D) no solution
Answer:
(D) no solution
Explanation:
We know that equa tion of I he form y — a is a line parallel to r-axis at a distance V from it. y = 0 is the equation of the r-axis and y = -7 is the equation of the line parallel to the .v-axis. So, these two equations represent two parallel lines. Therefore, there is no solution
Question 6.
One equation of a pair of dependent linear equations is -5x + 7y = 2. The second equation can be:
(A) 10x + 14y + 4 = 0
(B) -10x – 14y + 4 = 0
(C) -10x + 14y + 4 = 0
(D) 10x – 14y= – 4
Answer:
(D) 10x – 14y= – 4
Explanation:
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\)=\(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\)=\(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)=\(\frac{1}{k}\)
Given equation of line is, – 5x + 7y – 2 = 0
Here,a1 = – 5, b1 = 7, c1 = – 2
From EQuestion (i), – \(\frac{5}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{7}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{2}{c_{2}}=\) = \(\frac{1}{k}\)
⇒ a2 = – 5k, b2 = 7k, c2 = – 2k
where k is any arbitrary constant.
putting k =2, then a2 = – 10, b2 = =14 and c2 = – 4
⇒ The required equation of line becomes,
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0
⇒ – 10x + 14y – 4 = 0
⇒ 10x – 14y + 4 = 0
Question 7.
For what value of k, do the equations 3x – y + 8 =0 and 6x – ky = – 16 represent coincident lines
(A) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(B) \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
(C) 2
(D) -2
Answer:
(C) 2
Explanation:
3x – y = – 18
6x – ky = – 16
For coincident lince,
⇒ \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\)= \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{-1}{-k}\) \(\frac{-8}{-16}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{k}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 8.
If the lines given by 3x + 2ky = 2 and 2x + 5y + 1 = 0 are parallel, then the value of k is
(A) \(\frac{-5}{4}\)
(B) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(C) \(\frac{15}{4}\)
(D) \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Answer:
(C) \(\frac{15}{4}\)
Explanation:
For parallel lines (or no solution)
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3}{2}\) = \(\frac{2 k}{5} \neq \frac{-2}{1}\)
⇒ 4k = 15
⇒ k = \(\frac{15}{4}\)
![]()
Question 9.
A pair of linear equations which has a unique solution x = 2, y = -3 is:
(A) x + y = -1
2x – 3y = -5
(B) 2x + 5y = -11
4x + 10y = -22
(C) 2x-y = 1
3x + 2y = 0
(D) x-4y-14 = 0
x -y-13=0
Answer:
Option (B) & (D) is correct
Explanation:
(B) 2x + 5y = —11 and 4,r + 10y = -22
Put x = 2 and y = -3 in both the equations,
LHS = 2x + 5y ⇒ 2 x 2 + (-3)
⇒ 4- 15 = -11 = RHS
LHS = 4x + 10y -> 4(2) + 10(-3)
⇒8 – 30 – 22 = RHS
(D) x – 4y – 14 = 0 and 5x – y – 13 = 0
x – 4y = 14 and 5x – y = 13
Put x = 2 and y = -3 in both the equations,
LHS = x – 4y ⇒ 2 – 4(- 3) ⇒ 2 + 12 = 14 = RHS
LHS = 5x – y ⇒ 5(2) – (- 3) ⇒ 10 + 3 = 13 = RHS
Question 10.
Aruna has only ₹ 1 and ₹ 2 coins with her. If the total number of coins that she has is 50 and the amount of money with her is ₹ 75, then the number of ₹ 1 and ₹ 2 coins are, respectively
(A) 35 and 15
(B) 35 and 20
(C) 15 and 35
(D) 25 and 25
Answer:
(D) 25 and 25
Explanation:
Let the number of ₹ 1 coins = x and the number of ₹ 2 coins = y
So, according to the question,
x + y = 50 ………(i)
x + 2y =75 ………(ii)
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii),
y = 25
Substituting value of y in (i)x = 25
So, y = 25 and x = 25
Question 11.
The father’s age is six times his son’s age. Four years hence, the age of the father will be four times his son’s age. The present ages, in years, of the son and the father are, respectively:
(A) 4 and 24
(B) 5 and 30
(C) 6 and 36
(D) 3 and 24
Answer:
(C) 6 and 36
Explanation:
Let the present age of father be x years and the present age of son be y years.
∴ According to the question,
x = 6y …(i)
Age of the father after lour years = (x + 4) years
Age of son after four years = (y + 4) years Now, according to the question,
x + 4 = 4(y + 4)
x + 4 = 4(y + 4)
x +4 = 4y + 16
⇒ 6y – 4y = 16 – 4
⇒ 2y = 12
⇒ y = 6
x = 6 × 6 = 36 years
y = 6 years
So, the present ages of the son and the father are 6 yeaers and 36 years, respectiveiy.
![]()
Question 12.
If x = a, y = fa is the solution of the equations x – y = 2 and x + y = 4, then the values of a and fa are, respectively
(A) 3 and 5
(B) 5 and 3
(C) 3 and 1
(D) – 1 and 3
Answer:
(C) 3 and 1
Explanation:
If (a, b) is the solution of the given equations, then it must satisfy the given equations, so,
a – b = 2 ………(i)
17 a + b = 4 ……. (ii)
⇒ 2a = 6[Adding (i) and (ii) ]
⇒ a = 3
Now, 3 + 6 = 4
⇒ b = 1
So, (a, b) = (3, 1).
Question 13.
The larger of two supplementary angles exceed the smaller by 18°, then the angles are:
(A) 99°, 81°
(B) 98°, 82°
(C) 97°, 83°
(D) None of these.
Answer:
(A) 99°, 81°
Explanation:
Let one angle be x.
Then, other angle (it’s supplementary angle)
= (180° – x)
Given, x + 18° = (180° – x)
2x = 180° – 18°
2x = 162°
x = 81°
other angle = 180° – 81° = 99°
Hence two required angles are 81° and 99°
![]()
Question 14.
If 2x + 4 y = 23 and 4x – y = 19, then the values of ( 5y = 2x) \(\left(\frac{y}{x}-2\right)\) and are:
(A) \(30, \frac{5}{7}\)
(B) \(31, \frac{-5}{7}\)
(C) \(32, \frac{5}{7}\)
(D) None of these.
Answer:
(B) \(31, \frac{-5}{7}\)
Explanation:
Given,
2x + y = 23 …(i) and 4x – y = 19 …(ii)
On adding eQuestion (i) and (ii), we get
6x = 42 ⇒ x = 7
putting the value of x in eQuestion (i), we get
⇒14 + y =23
⇒y = 23 —14 = 9
Hence, 5y – 2x = 5 x 9 – 2 x 7 = 45 – 14 =31.
and \(\frac{y}{x}\) -2 = \(=\frac{9}{7}\) -2 = \(\frac{9-14}{7}\) = \(\frac{-5}{7}\)
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false and R is True
Question 1.
Assertion (A): If the pair of linear equations 3x 4 y = 3 and 6x 4 ky = 8 does not have a solution, then the value of k = 2.
Reason (R): If the pair of linear equations x 4 y – 4 = 0 and 2x 4 ky = 3 does not have a solution, then the value of k = 2.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
Given equation are:
3x + y – 3 = 0
6x + ky – 8 = 0
Comparing eQuestion (i) with a1 x + b1y + c1 = 0 and eq. (ii) with a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 we get,
a1 = 3, a2 = 6, b1 = 1 b2 = k, c1 = -3 and c2 = – 8 Sine, given equation has solution.
So,
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
⇒\(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{k} \neq \frac{-3}{-8}\)
⇒\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{k} \neq \frac{3}{8}\)
Either \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{k}\) or \(\frac{1}{k} \neq \frac{3}{8}\)
⇒k = 2 or \(k \neq \frac{3}{8}\)
henece, the value of k is 2. Thus assertion is correct.
In case of reason :
Given equation :
x + y – 4 = 0
2 x z + ky – 3 = 0
Here \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\),\(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{1}{k}\)
and \(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\) = \(\frac{-4}{-3}\) = \(\frac{4}{3}\)
System has solution
⇒\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) =\(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{k} \neq \frac{4}{3}\)
k =2 or k ⇒\(k \neq \frac{3}{4}\)
Hence, the value of k is 2.
Thus, reason is correct. Hence both assetion and reason are correct but reason is not the correc t explanation for assertion.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): For all real values of c, the pair of equations x – 2y = 8 and 5x – 10y = c have a unique solution.
Reason (R): Two lines are given to be parallel. The equation of one of the lines is 4x + 3y = 14,12x + 9y = 5.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is True
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
x -2y = 8
5x – 10 = c
⇒ \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\), \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{-2}{10}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\) and = \(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\) = \(\frac{-8}{-c}\)= \(=\frac{8}{c}\)
As \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\), so system of equations can never have unique solution.
∴ Assertion is incorrect.
In case of reason:
The equation of one line is 4x + 3y = 14. We know that if two lines a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 are parallel, then
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
or \(\frac{4}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{3}{b_{2}}\) =\(\frac{-14}{c_{2}}\)
⇒\(\frac{a_{2}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{4}{3}=\) \(\frac{12}{9}\)
hence one of the possible, second parallel line is 12 x + 9y = 5.
∴ Reason is correct.
Hence assetin is in correct but reason is correct.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): If the equation 3x – y + 8 = 0 and 6x – ky = -16 represent coincident lines, then the value of k = 2.
Reason (R): If the lines given by 3x + 2Ay = 2 and 2x + 5y + 1 = 0 are parallel, then the value of k is 15.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
3x – y = -18
6x – ky = -16
For coincident lines,
⇒ \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) =\(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{-1}{-k}\) = \(\frac{-8}{-16}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{k}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So, k = 2.
∴ Assertion is correct.
In case of reason:
For parallel lines ( or no solution)
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}\) = \(\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\) = \(\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3}{2}\) = \(\frac{2 k}{5}\) = \(\frac{-2}{1}\)
⇒ 4k = 15
⇒ k = \(\frac{15}{4}\)
∴ Reason is incorrect.
Hence, assertion is but reason is incorrect.
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): If 4 chairs and 3 tables cost ₹ 2100 and 5 chairs and 2 tables cost ₹ 1750, then the cost of 1 chair is ₹ 150.
Reason (R): Sum of the ages of a father and the son is 40 years. If father’s age is 3 times that of his son, then the son’s age is 12 years.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
Let cost of 1 chair be ₹ x and cost of 1 table be ₹ y
According to the question,
4x + +3y = 2100
5x + 2y = 1750
Multiplying eqn. (i) by 2and enQuestion (ii) by 3, we get
8x + 6y = 4200
15x + 6y = 5250
eqn. (iv) – eqn.(iii)
⇒ 7x = 1050
⇒x = 150
Substituting the value of x in (i) we gel y = 500 Thus, the cost of one chair and one table are ∴ 150 and ∴ 500 respectively.
∴ Assertion is correct. is
In case of reason:
Let age of father and son be x and y respectively.
Then, x + y =40 …(i)
and x = 3y …(ii)
By solving eqns. (i) and (ii), we get
x = 30 and y = 10
Thus, the ages of father and son are 30 years and 10 years.
∴ Reason is incorrect.
Hence, Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The solution of the pair of linear 19 equations x + y = 5 and 2x – 3y = 4 is x = \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{a}\)
Reason (R): The solution of the pair of linear equations 3x + 4y = 10 and 2x – 2y = 2 is x = 2 and y = 1.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
By elimination method,
x + y = 5 …(i)
2x – 3y —4 …(ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by (ii), we obtain
2x + 2y =10 …(iii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from equation (iii), we obtain
5y = 6
y = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
Substituting the value in equation (i), we obtain
x = 5 – \(\frac{6}{5}\) = \(\frac{19}{5}\)
x = \(\frac{19}{5}\),y =\(\frac{6}{5}\)
∴ Assertion is correct.
In case of reason:
By elimination method,
3x + 4y = 10
2x – 2y = 2
Multiplying equation (ii) by 2, we ob tain
4x – 4y = 4
Adding equstion (i) and (ii) , we obtain
7x = 14
x = 2
Substituting in equstion (i), we obtain
6 + 4y = 10
4y = 4
y = 1
x = 2, y = 1
∴ Reason is correct.
HEnce ,both assertion and reason aer correct but reasn is not the correct explanation for assertion
Question 6.
Assertion (A): In a AABC, ∠C = 3∠B = 2(∠A + ∠B), then ∠A = 20°.
Reason (R): The angles of a triangle are x, y and 40°. The difference between the two angles x and y is 30°, then A = 85° and y = 55°.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
Given Aial,
∠C = 3/B = 2(∠A + ∠B) 3∠B = 2(∠A +∠B)
3∠B = 2(∠A + 2∠B)
3∠B =2 ∠A + 2 ∠B
∠B = 2 ∠A
2 ∠A -∠B = 0 …(i)
We know that the sum ot the measures of all angles of a triangle is 180″. Therefore,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
∠A + ∠B + 3∠B = 180°
∠A + 4∠B = 180° …(ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by 4, we obtain
8∠A – 4∠B = 0 ……….(iii)
Adding equations (ii) and (iii), we obtain
9∠A = 180°
∠A = 20°
∴ Assertion is correct.
In case of reason:
Given that, A, y and 40°are the angels of a triangle.
x + y + 40° = 180°
[Since the sum of all the angels of a triangle is 180°]
⇒ x + y = 140° …(i)
Also, x – y =30° …(ii)
On adding Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
2x = 170°
⇒x = \(\frac{170^{\circ}}{2}\)
⇒ x = 85°
On putting x = 85° in EQuestion (i), we get
85° + y = 140°
y = 140° -85° = 55°
⇒ y = 55°
Hence, the required values of x and y are 85° and 55°, respectively.
∴ Reason is correct.
Hence, both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
Case – Based MCQs
Attempt any four sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
I. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
It is common that Governments revise travel fares from time to time based on various factors such as inflation (a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money) on different types of vehicles like auto, Rickshaws, taxis, Radio cab etc. The auto charges in a city comprise of a fixed charge together with the charge for the distance covered. Study the following situations.


| Name of the city | Distance travelled (km) | Amount paid (₹) |
| City A | 10 | 75 |
| 15 | 110 | |
| City B | 8 | 9 |
| 14 | 145 |
Situation 1: In city A, for a journey of 10 km, the charge paid is ₹ 75 and for a journey of 15 km, the charge paid is ₹ 110.
Situation 2: In a city B, for a journey of 8 km, the charge paid is ₹ 91 and for a journey of 14 km, the charge paid is ₹ 145.
Refer situation 1
Question 1.
If the fixed charges of auto rickshaw be ₹ x and the running charges be ₹ y km/hr, the pair of linear equations representing the situation is
(A) x + 10y = 110, x + 15y = 75
(B) x + 10y =75, x + 15y = 110
(C) 10x + y =110,15x + y = 75
(D) 10x + y = 75,15x + y =110
Answer:
(B) x + 10y =75, x + 15y = 110
Explanation:
According to given situation, we have
x + 10y = 75 …(i)
x + 15y = 110 …(ii)
Question 2.
A person travels a distance of 50 km. The amount he has to pay is
(A) ₹ 155
(B) ₹255
(C) ₹ 355
(D) ₹ 455
Answer:
(C) ₹ 355
Explanation:
Solving two equations,

Now, putting y= 7 in equation (i)
x – 10 x 7 =75′
y + 70 = 75
x =75 – 70
x = 5
Now, if a person travels a distance of 50 km then, amount
= x + 50y
= 5 + 50 x 7
= 5 + 350
= 355
Refer situation 2
![]()
Question 3.
What will a person have to pay for travelling a distance of 30 km ?
(A) ₹ 185
(B) ₹ 289
(C) ₹ 275
(D) ₹ 305
Answer:
(B) ₹ 289
Question 4.
The graph of lines representing the conditions are:
(situation 2)
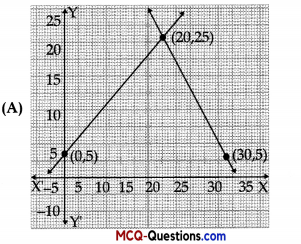
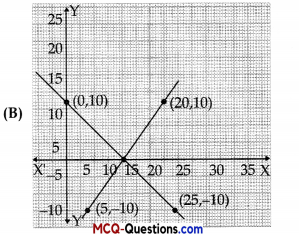
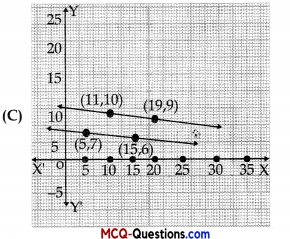
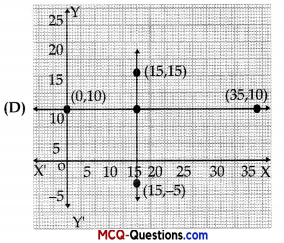
Answer:
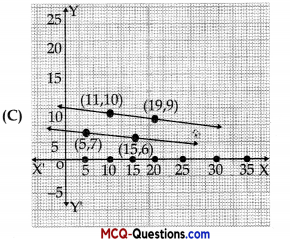
II. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Places A and B are 100 km apart on a highway. One car starts from A and another from B at the same time. If the cars travel in the same direction at different speeds, they meet in 5 hours. If they travel towards each other, they meet in 1 hour.
Question 1.
Assuming that the speed of first car and second car be u km/h and v km/h respectively.
What is the relative speed of both cars while they are travelling in the same direction ?
(A) (u + v) km/hr
(B) (u – v) km/hr
(C) (u/v) km/hr
(D) (uv) km/hr
Answer:
(B) (u – v) km/hr
Explanation:
Relative speed of both cars while they are travelling in same direction = (u – v) km/hr.
Question 2.
What is the relative speed of both cars while they are travelling towards each other ?
(A) (u + v) km/hr
(B) (u – v) km/hr
(C) (u/v) km/hr
(D) (uv) km/hr
Answer:
(A) (u + v) km/hr
Explanation:
Relative speed of both cars while they are travelling in opposite directions i.c., travelling towards each other = (u + v) km/hr.
Question 3
What is the actual speed of one car?
(A) 60 km/hr
(B) 40 km/hr
(C) 100 km/hr
(D) 20 km/hr
Answer:
(A) 60 km/hr
Explanation:
Let the speeds of first car and second car be u km/hr and’v km/hr respectively.
According to the given information.
5 (u – v) = 100
u – v = 20 „.(i)
u + v = 100 ……..(ii)
Soliving eqs. (i) and (ii),
we get u = 60 km/hr.
Question 4.
What is the actual speed of pther car?
(A) 60 km/hr
(B) 40 km/hr
(C) 100 km/hr
(D) 20 km/hr
Answer:
(B) 40 km/hr
Explanation:
Form above question 3, referring to the solution of both equations
v = 40 km/hr
Question 5.
The given problem is based on which mathematical concept
(A) Pair of linear equations
(B) Quadratic equations
(C) Polynomials
(D) none of the above
Answer:
(A) Pair of linear equations
Explanation:
The given problem is based on pair of linear equations.
III. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
John and Jivanti are playing with the marbles in the playground. They together have 45 marbles and John has 15 marbles more than Jivanti.

Question 1.
The number of marbles Jivanti had:
(A) 15
(B) 30
(C) 40
(D) 5
Answer:
(A) 15
Explanation:
Lei the no. of marbles, John and Jivanti have, be x and y respectively. According to the given information,
x + y = 45 ……..(i)
x – y =15 …(ii)
Solving eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
x = 30 and y = 15
Question 2.
The number of marbles John had:
(A) 40
(B) 30
(C) 15
(D) 20
Answer:
(B) 30
Explanation:
According to the solution of question 1, we get x = 30.
![]()
Question 3.
If 45 is replaced by 55 in the above case discussed in the question, then the number of marbles Jivanti have:
(A) 15
(B) 30
(C) 20
(D) 35
Answer:
(C) 20
Explanation:
According to given problem,
x + y = 55 …(i)
x – y = 15 …(ii)
Solving eqs.(i) and (ii), we get
x = 35 and y = 20.
Question 4.
According to the question 3, the number of marbles John have:
(A) 30
(B) 40
(C) 45
(D) 35
Answer:
(D) 35
Explanation:
From above question 3, we get x = 35. Hence, John had 35 marbles.
Question 5.
The given problem is based on which mathematical concept ?
(A) pair of linear equations
(B) Quadratic equations
(C) Polynomials
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) pair of linear equations
Explanation:
The given problem is based on pair of linear equations.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths with Answers
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Read More »




