Two Stories about Flying Class 10 MCQ Questions with Answers English Chapter 3
MCQ Questions for Class 10 English First Flight Chapter 3 Two Stories about Flying with Answers
![]()
I. The day before, all day long, he had watched his parents flying about with his brothers and sister, perfecting them in the art of flight, teaching them how to skim the waves and how to dive for fish. He had, in fact, seen his older brother catch his first herring and devour it, standing on a rock, while his parents circled arouxad raising a proud cackle. And all the morning the whole family had walked about on the big plateau midway down the opposite cliff taunting him with his cowardice.
Question 1.
Based on the given sentence, pick the option that corresponds to what human parents would say. ‘While his parents circled around raising a proud cackle.’
(A) Well done!
(B) Oh no!
(C) Ready?
(D) Really!
Answer:
(A) Well done!
Explanation:
‘Well done!’ is said to encourage the child after successfully doing something. ‘Oh No!’ will be Isaid if the child is not able to do something. ‘Ready?’ will be said before starting of the event and not after the completion. ‘Really!’ will be said when the parents do not expect or trust that their child will be able to do this.
![]()
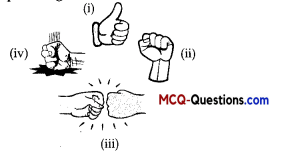
Question 2.
Which option lists the image nearest to ‘skim the waves’

(A) Image (i)
(B) Image (ii)
(C) Image (iii)
(D) Image (iv)
Answer:
(D) Image (iv)
Explanation:
‘Skim the waves’ means to test the level of movement of waves which is best depicted in option (D). In Option (A), there is no water around the bird, in (B) the bird is already swimming confidently in the ( water and in (G), the bird is flying high in the sky.
Question 3.
Imagine that the young gull attended a workshop on inspiration and confidence building and received a couple of pieces of advice.

Explanation:
The young bird knew that birds are meant to fly, so he already knew about himself. It also is not about how early or late he should start flying so as to benefit. The extract is about the young bird whose siblings had already learnt flying, but he was having the first flight, so he need not bother himself about what others were doing, it was important for the young bird as being the First flight. Also, he was earlier afraid of flying, but when he overcame his fear, he learnt the art of flying.
Question 4.
Which of the following feelings did the young gull, NOT feel according to the given context?
“…all day long, he had watched his parents flying about with his brothers and sister…”
(i) sad
(ii) incompetent
(iii) excluded
(iv) ungrateful
(v) inspired
(vi) jealous
(vii) anxious
(A) (i), (iii), (vi)
(B) (ii), (v), (vii)
(C) (ii), (iii), (vii)
(D) (iv), (v), (vi)
Answer:
(D) (iv), (v), (vi)
Explanation:
The young bord was full of feelings of sadness (for not able to enjoy flying from one place to another), incompetence (as he thought that he cannot fly), excluded (as others enjoyed in water and he used to sit alone outside) and anxious (as he also wanted to fly). However, he never felt ungrateful, inspired and jealous of his parents or siblings.
Question 5.
Select the most appropriate option for the following: devour: guzzle: nibble :
(A) chew
(B) savour
(C) peck
(D) gulp
Answer:
(C) peck
Explanation:
Devour and Guzzle refer to eating in big bites and quick swallowing. Nibble and Peck refer to eating in small tit bits and lazily eating. Chew refers to biting and grinding with teeth the bite taken. Savour refers to enjoying food. Gulp also refers to eating big bites and quick swallowing, so does not match with Nibble.
II. He just felt a bit dizzy. Then he flapped his wings once and he soared upwards. ”Ga, ga, ga, Ga, ga, ga, Gaw- col-ah,” his mother swooped past him, her wings making a loud noise. He answered her with another scream. Then his father flew over him screaming. He saw his two brothers and his sister flying around him curveting and banking and soaring and diving. Then he completely forgot that he had not always been able to fly, and commended himself to dive and soar and curve, shrieking shrilly.
![]()
Question 1.
Pick the most appropriate reason why the young gull felt dizzy.
(A) He hadn’t eaten anything for a day.
(B) He was dizzy with excitement.
(C) He was wary of heights.
(D) He was flying for the first time.
Answer:
(D) He was flying for the first time.
Explanation:
Dizzy here means giddy, a feeling which one experiences when someone is doing a new thing for the first time. Here, the young bird was flying for the first time.
Question 2.
How would you describe the screams of the gulls in the given extract?
(A) Elation
(B) Bewilderment
(C) Shock
(D) Protection
Answer:
(C) Shock
Explanation:
His parents were delighted and overjoyed, that is elated, when the young bird started flying. They were not bewildered or shocked (as they knew that he can fly). They were not trying to protect him by I flying over him, they were just expressing their joy.
![]()
Question 3.
The line “he completely forgot that he had not always been able to fly” implies the:
(A) great confidence the young gull had in his skills.
(B) naturalness of the act of flying for the young gull.
(C) satisfaction and joy of flying together as a family.
(D) desire of the young gull to leave his fears behind.
Answer:
(B) naturalness of the act of flying for the young gull.
Explanation:
Flying is natural to birds. It was just that the young bird learnt it later that the birds are made for flying.
Question 4.
The extract refers to the many movements of the young gull’s brothers and sister. Choose the option that correctly sequences these movements.
(A) The young gull’s brothers and sister flew by tilting their wings, rose high, made darting movements and plunged headfirst.
(B) The young gull’s brothers and sister flew by plunging headfirst, making darting movements, titled their wings and rose high.
(C) The young gull’s brothers and sister flew with darting movements’, titled their wings, rose high and plunged headfirst.
(D) The young gull’s brothers and sister flew by rising high, plunging headfirst, making darting movements and tilting their wings.
Answer:
(C) The young gull’s brothers and sister flew with darting movements’, titled their wings, rose high and plunged headfirst.
Explanation:
Curveting – flying with tilted wings, Banking – quick darting movements, Soaring – rising high in sky, Diving – plunging headfirst into water (to catch fish).
Question 5.
Which of the following mirrors the use of the literary device in “shrieking shrilly”?
(A) Sparkling saga
(B) Singing soft
(C) Slippery sloppily
(D) Sneeze silently
Answer:
(D) Sneeze silently
Explanation:
‘Shrieking shrilly’ and ‘Sneeze silently’ are use of alliterations.
(B) Black Aeroplane
I. Everything was going well — it was an easy flight. Paris was about 150 kilometers behind me when I saw the clouds. Storm clouds. They were huge. They looked like black mountains standing in front of me across the sky. 1 knew I could not fly up and over them, and I did not have enough fuel to fly around them to the north or south. “I ought to go back to Paris,” I thought, but I wanted to get home. 1 wanted that breakfast. ‘I’ll take the risk,’ I thought and flew that old Dakota straight into the storm.
Question 1.
Based on the given extract, choose the option that lists the name which would be the most appropriate response to “…it was an easy flight”?

(A) Option (i)
(B) Option (ii)
(C) Option (iii)
(D) Option (iv)
Answer:
(C) Option (iii)
Explanation: Before completing the flight, the narrator mentioned it as ‘an easy flight’. The later incidents show that the flight was full of adventure and suspense. So, ‘You spoke too soon’ is the best response to the comment.
Question 2.
How would you describe the “risk” the narrator took?
(A) Calculated
(B) Impetuous
(C) Unavoidable
(D) Navigable
Answer:
(B) Impetuous
Explanation:
Impetuous means impulsive or hasty. Flying the Dakota into the storm was an impulsive | decision. He could not calculate in advance the risk that he might have to face, it was avoidable as he could return to Paris and it was not navigable as he could not see far due to thick and heavy clouds.
![]()
Question 3.
In what way might the reference to the Dakota as “old” be relevant?
(A) Its antique value made it expensive and precious to the narrator.
(B) It is employed by the narrator as a term of endearment.
(C) It did not have enough fuel to fly around the storm clouds.
(D) Its ability to negotiate the storm clouds might have been suspected.
Answer:
(D) Its ability to negotiate the storm clouds might have been suspected.
Explanation:
‘Old’ here has been used to refer to its inability to stand heavy storms during flight as estimated by the narrator.
Question 4.
Read the statements given below, and then select the option that best describes the given statements.
Statement I – The narrator’s desire to reach home and see his family made him complacent.
Statement II – The narrator was unaware of the threat that the adversarial storm clouds presented.
Statement III – The narrator’s decision making was quick, but irresponsible as well as dangerous.
(A) Statement I is False, Statement II is True, Statement III cannot be inferred.
(B) Statement I and III are True, Statement II cannot be inferred.
(C) Statement I cannot be inferred, Statement II is False, Statement III is True.
(D) Statement I and II are False, Statement III is True.
Answer:
(C) Statement I cannot be inferred, Statement II is False, Statement III is True.
Explanation:
The passage does not mention that the narrator was content satisfied, that is complacent or not before reaching and meeting his family, so, Statement cannot be inferred. The narrator was aware of 8 the threat he might have to face. The phrases like ‘old Dakota’ and ‘ will take the risk’ indicate the fact. So, statement II is false. The narrator’s decision was impulsive, so statement III is true.
Question 5.
Select the correct option to fill in the blanks below
risk:……………. risky:…………..
(A) danger: dangerously
(B) hazard: hazardous
(C) peril: imperilled
(D) caution : precaution
Answer:
(B) hazard: hazardous
Explanation:
Following the pattern of risk: risky, the correct patterns would be danger: dangerous, hazard : hazardous, peril: perilous and caution: cautious. So, option (b) is correct.
![]()
II. I was safe! turned to look for my friend in the black aeroplane, but the sky was empty. There was nothing there. The black aeroplane was gone. i could not see it anywhere. I landed and was not sorry to walk away from the old Dakota near the control tower. I went and asked a woman in the control centre where I was and who the other pilot was. I wanted to say Thank you’. She looked at me very strangely, and then laughed. “Another aeroplane? Up there in this storm? No other aeroplanes were flying tonight. Yours was the only one I could see on the radar.” So, who helped me…
Question 1.
Select the option that correctly tracks the progression of emotions experienced by the narrator in the given extract.
(A) excited – surprised – relieved – grateful – perplexed
(B) relieved – confused – curious – dejected – panic-stricken
(C) optimistic – lonely – calm – elated – appreciative
(D) triumphant – reassured- inquisitive – thankful – uncertain
Answer:
(A) excited – surprised – relieved – grateful – perplexed
Explanation:
The correct track of expressions is excited (to come out of the storm), surprised (to see the empty sky and at absence of the black aeroplane), relieved (to land safely in old Dakota), grateful (towards the other pilot who guided him to safety) and perplexed (to know-that there were no other aeroplanes flying that night).
Question 2.
Why do you think the woman in the control centre laughed?
(A) She found the narrator funny.
(B) She thought his question preposterous.
(C) She thought he was teasing her.
(D) She was relieved the narrator was safe.
Answer:
(B) She thought his question preposterous.
Explanation:
She thought that the narrator was an experienced pilot and yet, he wanted to meet the other pilot, scheduled to land at the same time when there was no aeroplane in sight. So, she thought that he was trying to be funny. Preposterous means absurd, she had no sympathy with safe landing of narrator as she was not aware of the danger he had faced and he was surely not trying to tease her as indicated in the story.
Question 3.
Filled with questions, the narrator decides to place an advertisement in the local newspaper to look for his “friend”. Read the advertisement given below and select the option that includes the most appropriate solutions for the blanks:
Looking for a pilot of a black aeroplane who (i)…………. an old Dakota out of storm clouds late last night, but (ii)………….. before the Dakota pilot could express his gratitude after landing. Though control centre and radar did not (iii)…………….its presence, the Dakota pilot would really appreciate if his friend reached out. Please contact the Dakota pilot at 5200100110. In deep gratitude and eager (iv) ………….. XXX.
(A) (i) guided; (ii) disappeared; (iii) register; (iv) anticipation
(B) (i) took; (ii) landed; (iii) acknowledge; (iv) appreciation
(C) (i) brought; (ii) went away; (iii) confirm; (iv) expectation
(D) (i) helped; (ii) vanish; (iii) make note; (iv) excitement
Answer:
(C) (i) brought; (ii) went away; (iii) confirm; (iv) expectation
Explanation:
The black aeroplane helped and showed way – guided Later on, the narrator was not able to see the aeroplane because it – disappeared The radar and control centre did not know about its presence, they did not – registerThe narrator expected to hear about the pilot and the black aeroplane – anticipation
Question 4.
The narrator exclaimed that he was “safe”. Which of the following represented the most immediate threat to the narrator’s safety?
(A) The black mountain-like storm cloud
(B) The depletion of fuel in the last fuel tank
(C) Being lost due to non-functioning equipment
(D) The old rattling Dakota aeroplane
Answer:
(B) The depletion of fuel in the last fuel tank
Explanation:
The pilots are used to flying in bad weather conditions also, so storm cloud was not a major threat. The non-functioning equipment was also not a threat. The narrator was comfortable in flying the Dakota, so he was not afraid of that too. The near empty fuel tank was a major threat to the safety of the I narrator.
![]()
Question 5.
Choose the option that correctly matches the idioms in Column A to the story’s events in Column B:
| Column A – Idioms | Column B – Story events |
| 1. Every cloud has a silver lining. | (i) The narrator really wanted to have a hearty English breakfast, even though he really ought to have turned back. |
| 2. To be on cloud nine. | (ii) The man in the other plane waved at the narrator and asked him to follow closely, drawing him out. |
| 3. To have your head in the clouds. | (iii) The compass and other instruments stopped working. The radio was dead too. |
| 4. Gathering clouds. | (iv) And there it was – the well-lit runway. An airport. The narrator could safely land. |
1. Every cloud has a silver lining. (i) The narrator really wanted to have a hearty English breakfast, even though he really ought to have turned back.
2. To be on cloud nine. (ii) The man in the other plane waved at the narrator and asked him to follow closely, drawing him out.
3. To have your head in the clouds. (iii) The compass and other instruments stopped working. The radio was dead too.
4. Gathering clouds. (iv) And there it was – the well-lit runway. An airport. The narrator could safely land.
(A) l-(iv); 2-(iii); 3-(ii); 4-(i)
(B) l-(iii); 2-(i); 3-(iv); 4-(ii)
(C) l-(i); 2-(ii); 3-(iii); 4-(iv)
(D) l-(ii); 2-(iv); 3-(i); 4-(iii)
Answer:
(C) l-(i); 2-(ii); 3-(iii); 4-(iv)
Explanation:
Every cloud has a silver lining means – every difficult situation has some hope – the narrator was lost in storm clouds and the black aeroplane came to guide him. To being on cloud nine means – being elated or feeling too happy – the narrator saw the airport and runway and landed safely.To have your head in clouds means – being absent minded – the narrator should have turned back but absentmindedly moved forward to have a hearty breakfast at home.Gathering clouds means – upcoming dangers – the equipment of narrator’s plane have stopped working.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 English with Answers
Two Stories about Flying Class 10 MCQ Questions with Answers English Chapter 3 Read More »