Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 MCQ Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is not observed in a homologous series? Give reason for your choice.
(A) Change in chemical properties
(B) Difference in CH2 and 14u molecular mass
(C) Gradation in physical properties
(D) Same functional group
Answer:
(A) Change in chemical properties
Explanation:
Change in chemical properties due to presence of same functional group.
![]()
Question 2.
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(A) 6 covalent bonds
(B) 7 covalent bonds
(C) 8 covalent bonds
(D) 9 covalent bonds
Answer:
(B) 7 covalent bonds
Explanation:
Ethane has 7 covalent bonds. One bond is between two carbon atoms and rest of the six are between hydrogen atoms.
Question 3.
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g. hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
(A) helium
(B) neon
(C) argon
(D) krypton
Answer:
(B) neon
Explanation:
The nearest inert gas from carbon is Neon. An element try to attain the electronic configuration of its nearest noble gas while attaining a fully-filled outermost shell.
![]()
Question 4.
The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is

Answer:
(C) H :Q: H
Explanation:Oxygen has a complete after octet, while each atom of hydrogen has two electrons in outermost shell.
Question 5.
Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form fats. This is an example of
(A) Addition reaction
(B) Substitution reaction
(C) Displacement reaction
(D) Oxidation reaction
Answer:
(A) Addition reaction
Explanation:
Hydrogenation reaction means addition of hydrogen to double bonds of unsaturated compounds found in oil in the presence of catalysts such as palladium or nickel to give saturated hydrocarbons.
Question 6.
When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to ethanoic acid a gas evolves. Consider the following statements about the gas evolved.
(a) It turns lime water milky.
(b) It is evolved with a brisk effervescence.
(c) It has a smell of burning sulphur.
(d) It is also a byproduct of respiration.
The correct statements are :
(A) (a) and (b) only
(B) (b) and (d) only
(C) (a), (c) and (d)
(D) (a), (b) and (d)
Answer:
(D) (a), (b) and (d)
Explanation:
(a), (b) and (d). The gas evolved is carbon dioxide with brisk effervescence. It turns lime water milky. It is also a by-product of respiration.
![]()
Question 7.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(A) the food is not cooked completely.
(B) the fuel is not burning completely.
(C) the fuel is wet.
(D) the fuel is burning completely
Answer:
(B) the fuel is not burning completely.
Explanation:
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, then it means that the fuel is not burning completely.
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): In a homologous series of alcohols, the formula for the second member is C2H5OH and the third member is C3H7OH.
Reason (R): The difference between the molecular masses of the two consecutive members of a homologous series is 14u.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
In homologous series of alcohols, the formula for the second member is C2H5OH and the third member is C3H7OH. The difference between the molecular masses of the two consecutive members of a homologous series is 14u.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Following are the members of a homologous series :
CH3OH, CH3CFI2OH,CH3CH2CH2 OH
Reason (R): A series of compounds with same functional group but differing by CH2 unit is called a homologous series.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Following are the structural isomers of boutane.

Reason (R): Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in their structures.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Isomers are defined as those compounds that possess same molecular formula but different structural arrangement. Butane has the molecular formulae C<sub<4H<sub<10. Therefore, the structural isomers of butane will be n-butane and iso-butane.
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Third member of alkane is propane (C3H8)
Reason (R): It is obtained from general formula C2H2n + 2
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
C3H8 can be obtained from general formula, CnH2n+ 2.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): CH3Cl is obtained from CH4 by the action of Cl2 in the presence of sunlight.
Reason (R): It is obtained by addition reaction.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
CH3Cl is obtained from CH by substitution reaction by the action of Cl in the I presence of sunlight.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Most of the carbon compounds are good conductors of electricity.
Reason (R): They do not dissociate to form ions and remain as molecules.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Carbon compounds are mainly poor conductors of electricity.
Case-Based MCQs
Attempt any 4 sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
I. Read the passage and answer any four questions from Question l. to Question 5.
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH units in the main carbon chain.
Question 1.
The chemical properties of which of the following compounds is similar to the butane?
(A) Butyne
(B) Propene
(C) Propyne
(D) Pentane
Answer:
(D) Pentane
Explanation:
Methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series and have similar chemical properties.
Question 2.
The difference between two consecutive members in a homologous series in alkanes in terms of molecular mass and number of atoms of elements is:
(A) 14 a.m.u and CH2 respectively
(B) 12 a.m.u and CH3 respectively
(C) 14 a.m.u and CH respectively
(D) 12 a.m.u and CH3 respectively
Answer:
(A) 14 a.m.u and CH2 respectively
Explanation:
Homologous series is a series of compounds in which the members present have the same functional group and similar chemical properties and any two successive members in a particular series differ in their molecular formula by a CH2 unit.
Question 3.
The name and structure of a saturated compound in which 6 carbon atoms are arranged in a ring is :
(A) Hexane
(B) Cyclohexane
(C) Pentane
(D) cyclopentane
Answer:
(B) Cyclohexane
Explanation:
The series like methanol, ethanol, propanol and so on is also a homologous series. The functional group attached to these compounds is alcohol.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is not the property of a homologous series?
(A) They show similar chemical properties.
(B) They differ by 14 units by mass.
(C) They all contain double bond
(D) They can be represented by a general formula.
Answer:
(C) They all contain double bond
Explanation:
- The characteristics of a homologous series are:
- They have same general formula.
- Successive compounds differ by CH2 unit.
- Successive compounds have molecular mass difference of 14u.
- Molecular mass increases down the series. Therefore members of homologous series show gradation in physical properties such as melting point and boiling points.
- Members of homologous series show similar chemical properties.
Question 5.
Which of the following represent the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula Cn H2n + 2 ?
(A) Methane CH4
(B) Ethane C2H6
(C) Ethene C2H4
(D) Ethyne C2H6
Answer:
(B) Ethane C2 H6
Explanation:
Methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2.
II. Read the given passage and answer any of the four questions from Question l. to Question 5.
Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon.

Question 1.
Name the characteristic property of carbon as depicted in the fig. A
(A) Catenation
(B) Polymerisation
(C) Isomerisation
(D) None of the above.
Answer:
(A) Catenation
Explanation:
Carbon forms bond with other atoms of carbon. This property of carbon is known as catenation.
Question 2.
Carbon forms large number of compounds due to :
(A) Catenation only
(B) Tetravalency only
(C) Both catenation and tetravalency
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) Both catenation and tetravalency
Explanation:
Carbon forms large number of compounds due to the following:
(i) Catenation: Carbon forms bond with other atoms of carbon.
(ii) Tetravalency: Carbon share four electrons with other atoms.
Question 3.
Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which 6 carbon atoms are arranged in a ring.
(A) Hexane
(B) Cyclohexane
(C) Pentane
(D) cyclopentane
Answer:
(B) Cyclohexane
Explanation:
Cyclohexane is the carbon compounds in which carbon atoms are arranged in the form of a ring. It is a cyclic carbon compounds. Its structure is :
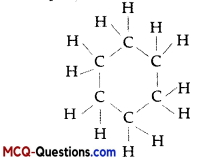
Question 4.
Give the number of single bonds present in the above mentioned compound.
(A) 16
(B) 14
(C) 6
(D) 18
Answer:
(D) 18
Explanation:
The chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between the atoms is known as a covalent bond. The total no. of single bonds in cyclohexane (C6H12) is 18.
![]()
Question 5.
Carbon is :
(A) Divalent
(B) Monovalent
(C) tetravalent
(D) Trivalent
Answer:
(C) tetravalent
Explanation:
Carbon has valency of four. It is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other monovalent element. Carbon can form bond with Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulphur, Chlorine and many other elements giving rise to compounds with specific properties.
III. Read the passage and answer any four questions Question l. to Question 5.
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C7H.Cl.
Question 1.
The compounds A, B and C are:
(A) A: ethene B: ethane C: chloroethane
(B) A: ethane B: ethyne C: chloromethane
(C) A: ethyne B: ethane C: chloroethane
(D) A: ethene B: ethyne C: chloroethane
Answer:
(A) A: ethene B: ethane C: chloroethane
Explanation:
The compound is A: CH2 = CH2 (Ethene), B is CH3—CH3(Ethane) and C is CH3—CH2—Cl (Chloroethane)
Question 2.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo…………… reaction.
(A) Substitution
(B) Halogenation
(C) Addition
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(C) Addition
Explanation:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. In unsaturated hydrocarbon, hydrogen added in the presence of catalyst palladium or nickel.
Question 3.
Which of these statements is correct regarding addition reaction?
(A) Addition of hydrogen does not require catalyst.
(B) Multiple bonds (double and triple bonds) must be present between carbon atoms in the chain of hydrocarbon.
(C) Multiple bonds are not required for the reaction to take place.
(D) None of the above.
Answer:
(B) Multiple bonds (double and triple bonds) must be present between carbon atoms in the chain of hydrocarbon.
Explanation:
Essential conditions required for the addition reaction to occur:
(i) Multiple bonds (double and triple bonds) must be present between carbon atoms in the chain of hydrocarbon.
(ii) Addition of hydrogen should be carried out in the presence of catalyst such as nickel or platinum.
![]()
Question 4.
The general formula for alkene is:
(A) CnH2n
(B) CnH2n+2
(C) CnH2n-2
(D) CnH2n+1
Answer:
(A) CnH2n
Explanation:
The General formula for alkenes are CnH2n, where n = number of carbon atoms. C2H4,C4H6,C4H8.
Question 5.
Choose the correct condition for conversion of ethene to ethane:
(A) Dehydrogenation at 450°C
(B) Hydrogenation in presence of catalyst like nickel or platinum
(C) Photolytic decomposition
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(B) Hydrogenation in presence of catalyst like nickel or platinum
Explanation:
Hydrogenation of ethene forms ethane in the presence of metal catalyst like Nickel at high temperature. This reaction is called hydrogenation reaction.

MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers