These NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming Ex 12.2 Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts. https://mcq-questions.com/ncert-solutions-for-class-12-maths-chapter-12-ex-12-2/
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming Exercise 12.2
![]()
Ex 12.2 Class 12 NCERT Solutions Question 1.
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contain at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs Rs 60/kg and Food Q costs Rs 80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/ kg of Vitamin A and 5 units/ kg of Vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of Vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
Solution:
Let the mixture contain x units of food P and y units of food Q. We have the data as

Vitamin A constaint: 3x + Ay ≥ 8
Vitamin B constraint: 5x + 2y ≥ 11
Cost function : Z = 60x + 80y
The L.P.P is Minimise Z = 60x + 80y
subject to the constraints 3x + 4y ≥8, 5x + 2y ≥ 11, x, y ≥ 0.

The feasible region is shaded in the figure and is unbounded.
We use comer point method to find the mini-mum of Z
From the table, the minimum value of Z is 160. Since the feasible region is unbounded j 160 may or may not be the minimum value i of Z. Consider the graph of the inequality 60x + 80y ≤ 160
i.e., 3x + 4y ≤ 8
This half plane has no point in common with the feasible region. Then the minimum value of Z is 160 at the points on the line segment joining A\(\frac { 8 }{ 3 }\), 0) and B(2, \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\))
Exercise 12.2 Class 12 Maths Ncert Solutions In Hindi Question 2.
One kind of cake requires 200 g of flour and 25g of fat, and another kind of cake requires 100 g of flour and 50 g of fat Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 5 kg of flour and 1 kg of fat assuming that there is no shortage of the other ingredients, used in making the cakes.
Solution:
Let x be the number of cakes of type I and y be the number of cakes of type II.
We make use of the following table to write the L.P.P.
We have the data as

Flour constraint: 200x + 100y ≤ 5000
i.e., 2x + y ≤ 50
Fat constraint: 25x + 50y ≤ 1000
i.e., x + 2y ≤ 40
Total number of cakes : Z = x + y
The L.P.P is Maximise Z = x + y
subject to the constraints
2x + y ≤ 50, x + 2y ≤ 40, x, y >0.

∴ Maximum value of Z is 30 at B(20, 10).
Hence maximum number of cakes is 30, of which 20 are of type 1 and 10 are of type II.
![]()
Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 NCERT Solutions Question 3.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman’s time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman’s time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftsman’s time.
i. What number of rackets and bats must be made if the factory is to work at full capacity?
ii. If the profit on a racket and on a bat is ₹ 20 and ₹ 10 respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works at full capacity.
Solution:
i. Let x be the number of tennis rackets and that y be the cricket bats.

Machine constraint: 1.5x + 3y ≤ 42
i.e., x + 2y ≤ 28
Craftman’s constraint: 3x + y ≤ 24
Profit function : Z = 20x + 10y
The L.P.P is Maximise Z = 20x + 10y subject to the constraints
x + 2y ≤ 28, 3x + y ≤ 24, x, y ≥ 0

∴ Maximum value of Z is 200 at B(4, 12).
Hence 4 tennis rackets and 12 cricket bats can be made if the factory is to work at full capacity.
ii. The maximum profit is ₹ 200/-
![]()
Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Question 4.
A manufacturer produces nuts and bolts. It takes 1 hour of work on machine A and 3 hours on machine B to produce a package of nuts. It takes 3 hours on machine A and 1 hour on machine B to produce a package of bolts. He earns a profit of ₹ 17.50 per package on nuts and ₹ 7.00 per package on bolts. How many package of each should be produced each day so as to maximise his profit, if he operates his machine for at the most 12 hours a day?
Solution:
Let x and y be the number of packages of nuts and bolts.
∴ We have the data as
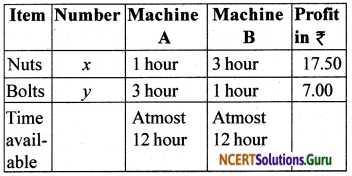
Machine A constraint: x + 3y ≤ 12
Machine B constraint: 3x + y ≤ 12
Profit function : Z = 17.5x + 7y
The L.P.P is maximise Z = 17.5x + 7y subject to the constraints 1x + 3y ≤ 12, 3x+ 1y ≤ 12, x, y > 0

Maximum value of Z is 73.50 at B(3, 3)
Hence the manufacturer must produce 3 packages of nuts and 3 packages of bolts to maximise his profit. The maximum profit is ₹ 73.50.
Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 Question 5.
A factory manufactures two types of screws, A and B. Each type of screw requires the use of two machines, an automatic and a hand operated. It takes 4 minutes on the automatic and 6 minutes on hand operated machines to manufacture a package of screws A, while it takes 6 minutes on automatic and 3 minutes on the hand operated machines to manufacture a package of screws B. Each machine is available for at the most 4 hours on any day. The manufacturer can sell a package of screws A at a profit of ₹ 7 and screws B at a profit of ₹ 10. Assuming that he can sell all the screws he manufactures, how many pack¬ages of each type should the factory owner produce in a day in order to maximise his profit? Determine the maximum profit.
Solution:
Let x be the number of packages of screw A and y be that of screw B.
We have the data as

Automatic machine constraint: 4x + 6y ≤ 240
Hand operated machine constraint: 6x + 3y ≤ 240
Profit function : Z = 7x + 10y
The L.P.P is maximise Z = 1x + 10y subject to the constraints 4x + 6y ≤ 240, 6x + 3y ≤ 240, x, y ≥ 0.

Maximum value of Z is 410 at B(30, 20).
Hence the factory should manufacture 30 packages of screw A and 20 packages of screw B to maximise the profit. The maxi-mum profit is ₹ 410.
Class 12 Chapter 12 Maths Ncert Solutions Question 6.
A cottage industry manufactures pedestal lamps and wooden shades, each requiring the use of a grinding/cutting machine and a sprayer. It takes 2 hours on grinding/cutting machine and 3 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a pedestal lamp. It takes 1 hour on the grinding/cutting machine and 2 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a shade. On any day, the sprayer is available for at the most 20 hours and the grinding/cutting ma-chine for at the most 12 hours. The profit from the sale of a lamp is ₹ 5 and that from a shade is ₹ 3. Assuming that the manufacturer can sell all the lamps and shades that he produces, how should he schedule his daily production in order to maximise his profit?
Solution:
Let the manufacturer produce x lamps and v wooden shades.

Grinding/cutting constraint: 2x + y ≤ 12
Sprayer constraint: 3x + 2y ≤ 20
Profit function : Z = 5x + 3y
∴ The L.P.P is maximise Z = 5x + 3y subject to the constraints 2x + y ≤ 12, 3x + 2y ≤ 20, x, y ≥ 0.
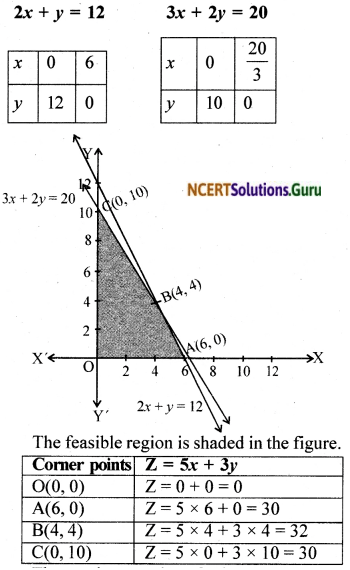
The maximum value of Z is 32 at B(4, 4). Hence to get maximum profit 4 pedestal lamps and 4 wooden shades are to be manufactured. The maximum profit obtained is ₹ 32.
![]()
Exercise 12.2 NCERT Solutions Question 7.
A company manufactures two types of novelty souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A require 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type B require 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours 20 minutes available for cutting and 4 hours for assembling. The profit is Rs 5 each for type A and Rs 6 each for type B souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should be company manufacture in order to maximise the profit?
Solution:
Let x be the number of souvenirs of type A and y be the number of souvenirs of type B to be manufactured.
We have the data as

Cutting constraint: 5x+ 8y ≤ 200
Assembling constraint: 10x + 8y ≤ 240
Profit function : Z = 5x + 6y
Then the L.P.P is maximise Z = 5x + 6y subject to the constraints 5x + 8y ≤ 200, 10x + 8y ≤ 240, x, y ≥ 0.

The maximum value of Z is 160 at B(8,20).
Hence for maximum profit 8 souvenirs of type A and 20 souvenirs of type B should be manufactured.
The maximum profit is ₹ 160.
Exercise 12.2 Class 12 NCERT Solutions Question 8.
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers – a desktop model and a portable model that will cost ₹ 25000 and ₹ 40000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant should stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than ₹ 70 lakhs and if his profit on the desktop model is ₹ 4500 and on portable model is ₹ 5000.
Solution:
Let the merchant plan to stock x desktop computers and y portable models.
We have the data as

Demand constraint: x + y ≤ 250
Cost constraint:
25000 x + 40000 y ≤ 7000000
i.e., 5x + 8 ≤ 1400
Profit function : Z = 4500x + 5000y
The L.P.P is maximise Z = 4500x + 5000y
subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 250, 5x + 8y ≤ 1400, x, y ≥ 0.
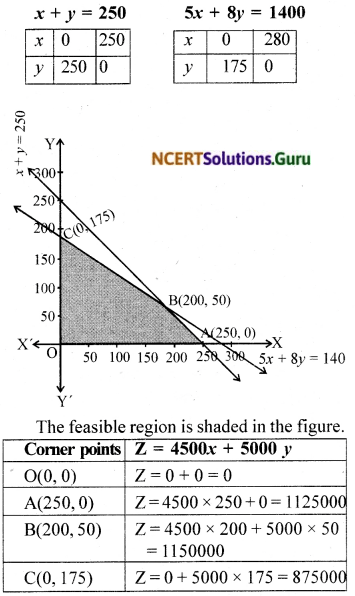
Maximum value of Z is 1150000 at B(200,50) Hence 200 desktop models and 50 portable models are to be stored to get maximum profit.
The maximum profit is ₹ 1150000.
![]()
12.2 Class 12 NCERT Solutions Question 9.
A diet is to contain atlest 80 units of vitamin A and 100 units of minerals. Two foods F1 and F2 are available. Food F1 costs ₹ 4 per unit food and F2 costs ₹ 6 per unit. One unit of food F1 contains 3 units of vitamin A and 4 units of minerals. One unit of food F2 contains 6 units of vitamin A and 3 units of minerals. Formulate this as a linear programming problem. Find the minimum cost for diet that consists of mixture of these two foods and also meets the minimal nutritional requirements.
Solution:
Let there be x units of food F1 and y units of food F2.
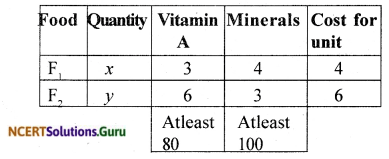
Vitamin A constraint: 3x + 6v ≥ 80
Minarals constraint: 4x + 3y ≥ 100
Cost function is : Z = 4x + 6y
The L.P.P is minimise Z = 4x + 6y subject to the constraints 3x + 6v ≥ 80,
4x + 3y ≥ 100, x,y ≥0.

From the table the minimum value of Z is 104. Since the region is unbounded, 104 may or may not be the minimum value of Z.
Consider the inequality 4x + 6y ≤ 104. This half plane has no point common with the feasible region. Hence the minimum value of Z is 104 at B (24, \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\))
∴ Minimum cost for diet is ₹ 104
Question 10.
There are two types of fertilisers F1 and F2F1 consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and F2 consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, a farmer finds that he needs atleast 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for her crop. If F1, costs ₹ 6/kg and F, costs ₹5/kg, determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
Solution:
Let x kg of fertilizer F1 and y kg of fertilizer
F2 be used.
We have the data as

Nitrogen constraint: 0.1 x + 0.05 y ≥ 14
i.e., 2x + y ≥ 280
Phosphoric acid constraint: 0.06x + 0.1 y ≥ 14
3x + 5y ≥ 700
Cost function : Z = 6x +5y
The L.P.P is minimise Z = 6x + 5y subject to the constraints 2x + y ≥ 280 and 3x + 5y ≥ 700, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0

From the table the minimum value of Z is 1000. Since the region is unbounded 1000 may or may not be the minimum value of Z.
Consider the inequality 6x + 5y ≤ 1000
This half plane has no point common with the feasible region
∴ Minimum value of Z is 1000 at B( 100,80).
Hence 100 kg of fertilizer F1 and 80 kg of fertilizer F2 is used. The minimum cost of these fertilizers is ₹ 1000.
![]()
Question 11.
The corner points of the feasible region de-termined by the following system of linear inequalities:
2x + y ≤ 10, x + 3y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 are (0, 0), (5, 0), (3, 4) and (0, 5). Let Z = px + qy, where р, q > 0. Condition on p and q so that the maximum of Z occurs at both (3, 4) and (0,5) is
a. p = q
b. p = 2q
с. p = 3q
d. q – 3p
Solution:
d. q – 3p
Since maximum Z occurs at (3, 4) and (0, 5), we get Z = 3p + 4q and Z = 0 + 5q
Since both values are same.
∴ 3p + 4q = 5q Hence 3p = q