MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
Management of Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ Questions With Answers
Question 1.
It was found that water from a river was contaminated with Coliform bacteria. Which one of the following pollutant might have got mixed with the water?
(A) Fertilizer run off
(B) Industrial waste
(C) Pesticides
(D) Human faecal matter.
Answer:
(D) Human faecal matter.
Explanation:
Coliform bacteria is a group of bacteria found in human intestine whose presence in water indicates contamination by disease causing micro-organisms.
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following stakeholders of forests causes the maximum damage to forest?
(A) People who live in or around the forest.
(B) The forest department of the government.
(C) The wildlife and native enthusiasts.
(D) The industrialists.
Answer:
(D) The industrialists.
Explanation:
Industrialists who use various forests produce for their factories causes the maximum damage to forest.
Question 3.
Soil fertility is determined by its ability to:
(A) Decay organic matter
(B) Hold organic matter
(C) Hold water
(D) Support life
Answer:
(D) Support life
Explanation:
Soil fertility is the ability of the soil to supply essential plant nutrients and soil water in adequate amounts for plant growth and reproduction, thereby support life.
Question 4.
The most appropriate definition of a natural resource is that it is a substance/commodity that is :
(A) present only on land.
(B) a gift of nature which is very useful to mankind.
(C) a man-made substance placed in nature.
(D) available only in the forest.
Answer:
(B) a gift of nature which is very useful to mankind.
Explanation:
Natural resource is a gift of nature which is very useful to mankind. Option (C) can be easily ruled out because natural resources are not man-made. Option (A) can be ruled out, because natural resources are present everywhere.
![]()
Question 5
The three R’s that will help us to conserve natural resources for long term use are
(A) recycle, regenerate, reuse
(B) reduce, regenerate, reuse
(C) reduce, reuse, redistribute
(D) reduce, recycle, reuse
Answer:
(D) reduce, recycle, reuse
Explanation:
The three R’s that will help us to conserve natural resources for long term use are reduce, recycle and reuse.
Question 6.
Given below are a few statements related to biodiversity. Pick those that correctly describe the concept of biodiversity.
(i) Biodiversity refers to the different species of flora and fauna present in an area
(ii) Biodiversity refers to only the flora of a given area
(iii) Biodiversity is greater in a forest
(iv) Biodiversity refers to the total number of individuals of a particular species living in an area
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (i) and (iii)
(D) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(C) (i) and (iii)
Explanation:
Both flora and fauna are included in biodiversity. Biodiversity is in greater degree in a forest. Hence, options (ii) and (iv) are incorrect.
Question 7.
The main cause for abundant coliform bacteria in the river Ganga is
(A) disposal of unbumt corpses into water.
(B) discharge of effluents from electroplating industries.
(C) washing of clothes.
(D) immersion of ashes.
Answer:
(A) disposal of unbumt corpses into water.
Explanation:
Coliform bacteria mainly come from human excreta, They can be present in unburnt corpses. Waste referred in other options does not contain human excreta.
Question 8.
A successful forest conservation strategy should involve
(A) protection of animals at the highest trophic level.
(B)protection of only consumers.
(C) protection of only herbivores.
(D) comprehensive programme to protect all the physical and biological components.
Answer:
(D) comprehensive programme to protect all the physical and biological components.
Explanation:
Protection of organisms at a single trophic level cannot maintain balance of our ecosystem. Hence, other options are ruled out.
Question 9.
Which one of the following is responsible for the sustenance of underground water?
(A) Loss of vegetation cover
(B) Diversion for high water demanding crops
(C) Pollution from urban wastes
(D) Afforestation
Answer:
(D) Afforestation
Explanation:
Afforestation (plantation of trees) will save ground water from getting depleted.
Question 10.
Incomplete combustion of coal and petroleum:
(i) increases air pollution.
(ii) increases efficiency of machines.
(iii) reduces global warming.
(iv) produce poisonous gases.
The correct option is:
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iv)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(B) (i) and (iv)
Explanation:
Incomplete combustion of coal and petroleum increases air pollution and produce poisonous gases.
Question 11.
Several factories were pouring their wastes in rivers A and B. Water samples were collected from these two rivers. It was observed that sample collected from river A was acidic while that of river B was basic. The factories located near A and B are:
(A) Soaps and detergents factories near A and alcohol distillery near B.
(B) Soaps and detergents factories near B and alcohol distillery near A.
(C) Lead storage battery manufacturing factories near A and soaps and detergents factories near B.
(D) Lead storage battery manufacturing factories near B and soaps and detergents factories near
Answer:
(D) Lead storage battery manufacturing factories near B and soaps and detergents factories near
Explanation:
Lead storage battery manufacturing factories near A and soaps and detergents factories near B led to the given observation.
Question 12.
Opposition to the construction of large dams is due to
(A) social reasons.
(B) economic reasons.
(C) environmental reasons.
(D) all the above.
Answer:
(D) all the above.
Explanation:
Dam construction adversely affects local flora and fauna by raising social, economic and environmental problems.
![]()
Question 13.
Pick the right combination of terms which has no fossil fuel.
(A) Wind, ocean and coal
(B) Kerosene, wind and tide
(C) Wind, wood, sun
(D) Petroleum, wood, sun
Answer:
(C) Wind, wood, sun
Explanation:
Wind, sun and wood are natural resources.
Question 14.
It is important to make small check dams across the flooded gullies because they
(i) hold water for irrigation.
(ii) hold water and prevent soil erosion.
(iii) recharge ground water.
(iv) hold water permanently.
(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv)
(D) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(B) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation:
Small check dams or temporary dams across the flooded gullies helps to prevent adverse effects of flooding on nearby areas and land.
Question 15.
Ground water will not be depleted due to
(A) afforestation.
(B) thermal power plants.
(C) loss of forest, and decreased rainfall.
(D) cropping of high water demanding crops.
Answer:
(A) afforestation.
Explanation:
Plantation of tree is called as afforestation. Afforestation conserves the soil moisture and allows the run-off water to infiltrate into ground water thereby adding to ground water recharge.
Question 16.
Khadins, Bundhis, Ahars and Kattas are ancient structures that are examples for
(A) grain storage.
(B) wood storage.
(C) water harvesting.
(D) soil conservation.
Answer:
(C) water harvesting.
Explanation:
Khadins, Bundhis, Ahara and Kattas are ancient water conservation practices.
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): We need to conserve natural resources.
Reason (R): Natural resources are limited.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
We need to manage natural resources because natural resources are limited. Human population is increasing at a tremendous rate and utilization of natural resources is increasing at an exponential rate. Therefore, we need to conserve resources for future generations.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Reuse is better than recycle.
Reason (R): Recycle prevents environmental pollution.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Reuse is better than recycle because it saves energy by using material again without any changes and also, it prevents environmental pollution.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The development which can be maintained for a long time without undue damage to the environment is called sustainable development.
Reason (R): It provide the economic well being to the present and future generation.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Sustainable development is the development which can be maintained for a longtime without undue damage to the environment. It has two main objectives: To provide economic well being to the present and future generations and to maintain a healthy environment and life support system.
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Chipko Andolan was done by women of Reni village.
Reason (R): Chipko Andolan was done to protect wild life.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Chipko movement was started in early 1970s in village Reni in Garhwal by the women of Uttarakhand to stop cutting of forest trees of their area.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Wildlife should be conserved.
Reason (R): Human activities cause several plants and animals to extinct.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Wild life is found in forests. Over a period of time, wildlife has become extinct because of certain human activities like deforestation, hunting, poaching etc.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Coliform is a group of bacteria found in human stomach.
Reason (R): Presence of coliform in water indicates contamination by disease causing microorganisms.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Coliform is a group of bacteria found in human intestine whose presence in water indicates contamination by disease causing micro-organisms.
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Water is a valuable resource.
Reason (R): Turn off the taps when not in use.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Water is a valuable resource. So, we need to conserve it by turning off the taps when not in use.
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Coal and petroleum are categorised as natural resources, so should be used judiciously.
Reason (R): They are formed from the degradation of biomass subjected to various biological and geological processes over a million of years.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Coal and petroleum are formed from the degradation of biomass subjected to various biological and geological processes over a million of years. Thus, cannot be manufactured by humAnswer:Therefore, coal and petroleum are categorised as natural resource.
Question 9.
Assertion (A): Water harvesting is the method to capture every trickle of water that falls on the land.
Reason (R): Water harvesting recharges wells and ground water.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Water harvesting is a technique of capturing rain water when it falls and taking measure to keep the water clean. It recharges wells/ground water and provides moisture for vegetation over a wide area.
![]()
Question 10.
Assertion (A): Bundhis are found in Rajasthan.
Reason (R): Bundhis are traditional water harvesting structures.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Bundhis are found in Madhya Pradesh whereas in Rajasthan, Khadins and nadis are found. They all are ancient water conservation practices.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Case-Based MCQs
Attempt any 4 sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
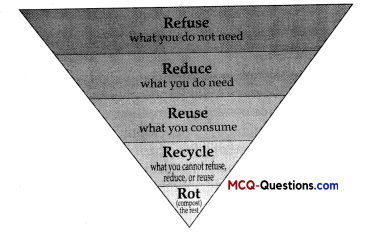
I. Observe the following diagram and answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
Question 1.
Choose the waste management strategy that is matched with correct example.
| (A) Refuse | Choose products that use less packaging |
| (B) Reduce | Give unwanted toys and books to hospitals or schools |
| (C) Reuse | Not using single use plastic |
| (D) Repurpose | Making flower pot from used plastic bottle |
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation:
Reusing a waste material to make something that is useful is called repurposing. Using a plastic bottle to make a flower pot is thus repurposing.
Question 2.
Recycling of paper is a good practice but recycled paper should not be used as food packaging because
(A) recycled papers may release color /dyes on food items
(B) recycled papers are not absorbent
(C) recycled papers can cause infection due to release of methane
(D) recycled papers are costly
Answer:
(B) recycled papers are not absorbent
Explanation:
It is because decomposition of paper produces chemicals like methane which may cause infection.
Question 3.
According to the ‘Solid Waste Management Rule 2016’, the waste should be segregated into three categories. Observe the table below and select the row that has correct information
| Wet waste | Dry waste | Hazardous waste |
| (A) Cooked food, vegetable peels | Used bulbs, fluorescent lamps | Plastic carry bags, bottles, newspaper, cardboard |
| (B) Coffee and tea powder, garden waste | Plastic carry bags, bottles, newspaper, cardboard | Expired medicines, razors, paint cans |
| (C) Leftover food, vegetable peels | Coffee and tea powder, garden waste | Insect repellents,cleaning solutions |
| (D) Uncooked food, tea leaves | Old crockery, frying pans | Coffee and tea powder, garden waste |
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation:
Coffee and tea powder, garden waste are recyclable wet waste, plastic carry bags, bottles, newspaper, cardboard are kitchen dry waste while expired medicines, razors, paint cans are domestic hazardous wastes.
Question 4.
Effective segregation of wastes at the point of generation is very important. Select the appropriate statements giving the importance of waste segregation.
(i) less waste goes to the landfills
(ii) better for public health and the environment
(iii) help in reducing the waste
(iv) resulting in deterioration of a waste picker’s health
(A) both (i) and (ii)
(B) both (i) and (iii)
(C) both (ii) and (iii)
(D) both (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(A) both (i) and (ii)
Explanation:
Waste segregation is included in law because it is much easier to recycle. Effective segregation of wastes means that less waste goes to landfill which makes it cheaper and better for people and the environment. It is also important to segregate for public health.
Question 5.
When recycling a plastic water bottle, what should you do with the cap?
(A) The cap goes into a garbage can and the bottle goes in a recycling bin
(B) Screw the cap back on the bottle, then put the bottle and cap in a recycling bin
(C) Screw the cap back on the bottle, then put the bottle and cap in the garbage can
(D) Recycle the cap separately.
Answer:
(A) The cap goes into a garbage can and the bottle goes in a recycling bin
Explanation:
The bottle cap goes into a garbage can and the bottle goes in a recycling bin.
II. Study the passage and answer any of the four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
Management and conservation of natural resources means the scientific utilization of resources. This method yields the greatest sustainable benefit of available resources to the present generations, while maintaining its potential to meet the needs and aspirations of future generations. In recent years, it has been observed that most of our natural resources are being depleted. It is mainly due to the over exploitation of resources as a result of changing lifestyle, over population and technological development. Thus the need of the hour is to wisely manage our natural resources and minimize their wastage. For this, we should remember the 3 R’s that can save environment.
Question 1.
Which of the following R’s is not used to save the environment?
(A) Reduce
(B) Remove
(C) Recycle
(D) Reuse
Answer:
(B) Remove
Explanation:
Remove is not the 3 R’s that can g save the environment.
Question 2.
Conservation is:
(A) Proper use of natural resources
(B) Protection of natural resources
(C) Utilisation of natural resources
(D) All of these.
Answer:
(A) Proper use of natural resources
Explanation:
Proper management of natural resources is essential for judicial use and conservation of natural resources.
![]()
Question 3.
If we are using discarded items of paper, plastic and sending them to the respective industries for making useful objects. Then which R to save the environment we are following?
(A) Reuse
(B) Remove
(C) Recycle
(D) Reduce
Answer:
(C) Recycle
Explanation:
We are using recycle method to save the environment.
Question 4.
Which of these you would practice in your daily life?
(A) Reuse
(B) Recycle
(C) Reduce
(D) Remove
Answer:
(A) Reuse
Explanation:
Reuse, because process of recycling uses some energy and takes some time.
Question 5.
Which of these statements is incorrect about sustainable development ?
(A) Economic development is linked to environmental conservation
(B) Sustainable development encourages development for current generation and conservation of resources for future generations
(C) Sustainable development does not consider the view points of stakeholders
(D) Sustainable development is a long planned and persistent development
Answer:
(C) Sustainable development does not consider the view points of stakeholders
Explanation:
Sustainable developments take into consideration both economic growth and ecological conservation simultaneously besides giving due considerations to the viewpoint any four stakeholders.
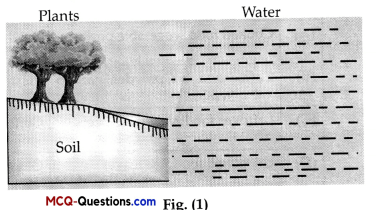
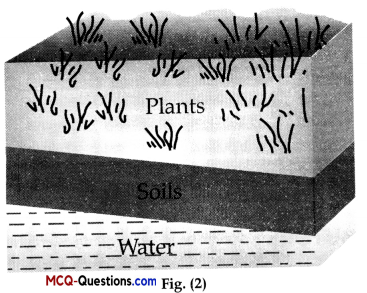
III. Study the given diagrams and answer any of the four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
Question 1.
The water reservoir in fig (1) and (2) is………….. and…………… respectively.
(A) Pond, underground water body
(B) Underground water body, pond
(C) Underground water body in both
(D) Pond in both
Answer:
(A) Pond, underground water body
Explanation:
In fig (1), the water reservoir is a pond while in fig (2), it is underground water body.
Question 2.
Which has an advantage over the other?
(A) Fig (1) has more advantage than fig (2).
(B) Fig (2) has more advantage than fig (1)
(C) Both has equal advantage.
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Fig (2) has more advantage than fig (1)
Explanation:
Fig (2) has more advantage than fig (1). It is because, ground water does not evaporate. It provides moisture for vegetation over a wide area. It is also protected from contamination by animal and human wastes.
Question 3.
Which of these reservoirs contains the most water?
(A) Atmosphere
(B) Biosphere
(C) Groundwater
(D) Lakes and rivers.
Answer:
(C) Groundwater
Explanation:
Ground water is the water that seeps through rocks and soil and is stored below the ground.
Question 4.
Ground water will not be depleted due to:
(A) Afforestation
(B) thermal power plants
(C) loss of forest, and decreased rainfall
(D) cropping of high water demanding crops
Answer:
(A) Afforestation
Explanation:
Afforestation (plantation of trees) will save ground water from getting depleted.
![]()
Question 5.
Khadins, Bundhis, Ahars and Kattas are ancient structures that are examples for
(A) grain storage.
(B) wood storage.
(C) water harvesting.
(D) soil conservation.
Answer:
(C) water harvesting.
Explanation:
Khadins, Bundhis, Ahars and Kattas are ancient water conservation practices.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources Read More »