Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ Questions With Answers
Question 1.
The laws of reflection hold true for:
(A) plane mirrors only
(B) concave mirrors only
(C) convex mirrors only
(D) all reflecting surfaces
Answer:
(D) all reflecting surfaces
Explanation:
The laws of reflection hold true for all reflecting surfaces.
![]()
Question 2.
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is:
(A) real
(B) inverted
(C) virtual and inverted
(D) virtual and erect
Answer:
(D) virtual and erect
Explanation:
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is virtual and erect.
Question 3.
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(i) cannot be projected on the screen
(ii) are formed by both concave and convex lens
(iii) are always erect
(iv) are always inverted The correct properties are:
(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (i) and (ii)
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Explanation:
A virtual image is formed when reflected rays appear to meet. Such images cannot be obtained on screen. Plane mirrors, convex mirror and concave lens always forms virtual image. They are always erect.
Question 4.
A real image is formed by the light rays after reflection or refraction when they:
(i) actually meet or intersect with each other.
(ii) actually converge at a point.
(iii)appear to meet when they are produced in the backward direction.
(iv) appear to diverge from a point.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (i) and (ii)
(D) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(C) (i) and (ii)
Explanation:
A real image is formed when light rays actually meet or intersect at a point after reflection or refraction.
Question 5.
The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1,2, 3 and 4 is:
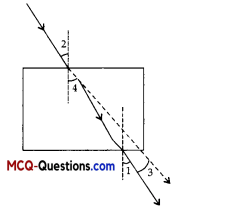
(A) 2,4,1, 3
(B) 2,1, 4, 3
(C) 1, 2, 4, 3
(D) 2,1, 3, 4
Answer:
(B) 2,1, 4, 3
Explanation:
Angle 2 is angle of incidence, as it is formed between the incident ray and the normal.Angle is angle of emergence, as it is formed between the emergent ray with normal. Angle 4 is angle of reflection as it is formed between the refracted ray and the normal. 3 shows the lateral displacement. Hence, the correct answer is 2,1,4,3.
![]()
Question 6.
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building about 1 km far from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen the student should slightly move the:
(A) mirror away from the screen
(B) screen away from the mirror
(C) screen towards the mirror
(D) screen towards the building
Answer:
(C) screen towards the mirror
Explanation:
The object is at infinity , so to Obtain sharp image screen should be moved towards mirror.
Question 7.
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab:

(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Answer:
(D) S
Explanation:
Among the given options, S will the most suitable set up for tracing a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
Question 8.
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the screen, as compared to the object is always:
(A) Laterally inverted and diminished
(B) Inverted and diminished
(C) Erect and diminished
(D) Erect and highly diminished
Answer:
(B) Inverted and diminished
Explanation:
When the object is at infinity, diminished, inverted and real image is formed.
Question 9.
In your laboratory you trace the path of light rays through a glass slab for different values of angle of incidence (∠i) and in each case measure the values of the corresponding angle of refraction (∠r) and angle of emergence (∠e).
On the basis of your observation your correct conclusion is:
(A) ∠i is more than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(B) ∠i is less than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(C) ∠i is more than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
(D) ∠i is less than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
Answer:
(A) ∠i is more than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
Explanation:
When a ray of light passes through the glass slab, then the angle of incidence is found to be nearly equal to angle of emergence and greater than angle of refraction.
Question 10.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
(A) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
(B) Convex mirror as well as concave lens
(C) Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other
(D) Concave mirror as well as concave lens
Answer:
(A) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
Explanation:
When a point source of light is placed at the focus of concave mirror then all light rays after reflection through mirror will become parallel to the principal axis.
When this point source of light is placed at the focus of convex lens then after refraction by light rays convex lens will become parallel to the principal axis.
![]()
Question 11.
Magnification produced by a rear-view mirror fitted in vehicles
(A) is less than one.
(B) is more than one.
(C) is equal to one.
(D) can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in front of it.
Answer:
(A) is less than one.
Explanation:
Convex mirror is used as rear¬view mirror in vehicles. It forms virtual, erect, and diminished images of the objects. Magnification is ratio of height of image to the height of the object, hence, magnification produced by a rear-view mirror fitted in vehicles is less than one.
Question 12.
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(A) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(B) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(C) Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(D) More than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer:
(B) 30 cm in front of the mirror
Explanation:
The distance of the sun is infinite as compared to the radius of curvature of concave mirror, so, light rays from sun incident parallel all the rays converge at the principal focus. So, the focal length is 15 cm. In case of a concave mirror, the size of image and object will be same if the object is placed at 2f. Hence, in this case object must be placed at 2/or 2×15 = 30 cm.
Question 13.
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed
(A) between the pole and the focus of the reflector.
(B) very near to the focus of the reflector.
(C) between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector.
(D) at the centre of curvature of the reflector.
Answer:
(B) very near to the focus of the reflector.
Explanation:
The rays of light passing through the principal focus will go parallel to principal axis after reflection thus, forming a concentrated beam of light. So, due to this reason in torches, search lights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed very near to the focus of the reflector.
Question 14.
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?


(A) Fig. A
(B) Fig. B
(C) Fig. C
(D) Fig. D
Answer:
(D) Fig. D
Explanation:
In case of concave mirror, an incident ray parallel to principle axis passes through F after reflection.
Question 15.
A student determines the focal length of a device ‘X’ by focussing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object. The device ‘X’ is
(A) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(B) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(C) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Answer:
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Explanation:
Image formed by the concave mirror in this case is same as when object is at infinity. Due to the great distance, light rays will incident almost parallel to principal axis. After reflection all the rays will converge and meet at principal focus. So, focal length is 20 cm.
Question 16.
A student obtains a blurred image of a distant object on a screen using a convex lens. To obtain a distinct image on the screen he should move the lens
(A) away from the screen
(B) towards the screen
(C) to a position very far away from the screen
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object
Answer:
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object
Explanation:
The incident rays coming from the distant object will be parallel to the principal axis and as we know the rays parallel to the principal axis, after refraction by convex lens, will pass through the principal focus. Hence, a distinct image will be obtained immediately when distance between screen and lens is equal to focal length, so option (D) is correct choice.
![]()
Question 17.
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence (∠i). He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction (∠r) and the angle of emergence (∠e) for every value of the angle of incidence. On analyzing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
(A) ∠i > ∠r > ∠e
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
(C) ∠i < ∠r < ∠e
(D) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
Answer:
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
Explanation:
(Angle of incidence) ∠i = ∠e (angle of emergence) because the direction of incident ray and emergent ray is parallel to each other.
∠e >∠r (angle of refraction) because at point of emergence light is entering into optically rarer medium (air) from optically denser medium (glass), so light will bend away from the normal making the angle bigger.
Question 18.
An optical device has been given to a student and he determines its focal length by focusing the image of the sun on a screen placed 24 cm from the device on the same side as the sun. Select the correct statement about the device
(A) Convex mirror of focal length 12 cm
(B) Convex lens of focal length 24 cm
(C) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
(D) Convex lens of focal length 12 cm
Answer:
(C) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
Explanation:
Because the screen is on the same side of the object which means it cannot be a lens because it happens behind the lenses in such case. Moreover, concave mirror forms real images, that is, image can be obtained on a screen.
Question 19.
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
Answer:
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
Question 20.
A student obtains a blurred image of a distant object on a screen using a convex lens. To obtain a distinct image on the screen he should move the lens:
(A) away from the screen
(B) towards the screen
(C) to a position very far away from the screen
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object.
Answer:
(D) either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object.
Question 21.
A teacher sets up the stand carrying a convex lens of focal length 15 cm at 42.7 cm mark on the optical bench. He asks four students A, B, C and D to suggest the position of screen on the optical bench so that a distinct image of a distant tree is obtained almost immediately on it. The positions suggested by the students were as :
(i) 12.7 cm
(ii) 29.7 cm
(iii) 57.7 cm
(iv) 72.7 cm
The correct position of the screen was suggested by
(A) (i)
(B) (ii)
(C) (iii)
(D) (iv)
Answer:
(C) (iii)
Explanation:
The incident rays coming from the distant tree placed will be parallel to the principal axis and as we know the rays parallel to the principal axis, after refraction by convex lens, will pass through the principal focus. Hence, a distinct image will be obtained immediately when distance between screen and lens is equal to focal length. 42.7 cm (position of lens on optical bench) + 15 cm (focal length of lens) = 57.7 (the position of screen on optical bench)
Question 22.
To determine the approximate focal length of the given convex lens by focussing a distant object (say, a sign board), you try to focus the image of the object on a screen. The image you obtain on the screen is always
(A) erect and laterally inverted
(B) erect and diminished
(C) inverted and diminished
(D) virtual, inverted and diminished
Answer:
(C) inverted and diminished
Explanation:
The image formed by lens will be inverted and diminished.
![]()
Question 23.
Suppose you have focussed on a screen the image of candle flame placed at the farthest end of the laboratory table using a convex lens. If your teacher suggests you to focus the parallel rays of sun, reaching your laboratory table, on the same screen, what you are expected to do is to move the:
(A) lens slightly towards the screen
(B) lens slightly away from the screen
(C) lens slightly towards the sun
(D) lens and screen both towards the sun
Explanation:
The candle is at the farthest end of the laboratory. SO, it may be considered at a distance greater that 2Fj and hence the image of formed between F2 and ZF2. when the sun will be focussed, the image will be formed as F2. SO, the lens is to the shifted towards the screen.
Question 24.
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be
(A) both concave.
(B) both convex.
(C) the mirror is concave and the lens is convex.
(D) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave. R
Answer:
(A) both concave.
Explanation:
As per the sign convention, the focal length of a concave mirror and a concave lens are taken as negative. Hence, both the spherical mirror and the thin spherical lens are concave in nature.
Question 25.
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
(A) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(B) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(C) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(D) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Answer:
(C) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
Explanation:
A magnified image of an object will be obtained when it is placed between the optical centre and focus of a convex lens. Magnification is also higher for convex lenses having shorter focal length. Therefore, for reading small letters, a convex lens of focal length 5 cm should be used.
Question 26.
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is

(A) \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(B) \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(C) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(D) \(\sqrt{2}\)
Answer:
(A) \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Explanation:
Here, angle of incidence = 60° Angle of refraction = r = 45° Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A
=nBA= \(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}\) = \(\frac{\sin 60^{\circ}}{\sin 45^{\circ}}\)
= \(=\frac{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}{\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)}\)= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Question 27.
A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in the figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be

(A) Greater than unity
(B) Less than unity
(C) Equal to unity
(D) Zero
Answer:
(A) Greater than unity
Explanation:
Since, light rays in medium B go towards normal, so it has greater refractive index and lesser velocity of light with respect to medium A. So refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A is greater than unity.
Question 28.
Which of the following statements is true?
(A) A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(B) A convex lens has – 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(C) A concave lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(D) A concave lens has – 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
Answer:
(A) A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
Explanation:
The power (P) of a lens of focal length (f) is given by P = 1/f where f is the focal length meter and power in dioptre.
Now, p = 1/f
or \(4=\frac{1}{f}\)
or \(f=\frac{1}{4} \mathrm{~m}\)=0.25m
Assertion and Reason Based Mcqs
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is True
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Plane mirror may form real image.
Reason (R): Plane mirror forms virtual image, if object is real.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Plane mirror may form real image, if object is virtual.

Question 2.
Assertion (A): The focal length of the convex mirror will increase, if the mirror is placed in water.
Reason (R): The focal length of a convex mirror of radius R is equal to, f = \(\frac{R}{2}\)
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is True
Explanation:
Focal length of the spherical mirror does not depend on the medium in which it is placed.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual.
Reason (R): The image formed by a concave mirror is certainly virtual if the object is real.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
The image of real object may be real in case of concave mirror.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): An object is placed at a distance of from a convex mirror of focal length its image will form at infinity.
Reason (R): The distance of image in convex mirror can never be infinity.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is True
Explanation:
The distance of image in convex I mirror is always finite.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): If the rays are diverging after emerging from a lens; the lens must be concave.
Reason (R): The convex lens can give diverging rays.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is True
Explanation:
If the rays cross focal point of convex lens, they become diverging.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Refractive index of glass with respect to air is different for red light and violet light.
Reason (R): Refractive index of a pair of media depends on the wavelength of light used.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Refractive index of any pair of media is inversely proportional to wavelength of light.
Hence, λv < λr
so, µr < µv
where, λv and < λr are the wavelengths of violet and red light.µr and < µv are refractive index of violet and red light.
![]()
Question 7.
Assertion (A): The refractive index of diamond is √6 and refractive index of a liquid is S. If the light travels from diamond to the liquid, it will be initially reflected when the angle of incidence is 30°. 1
Reason (R):\(\mu=\frac{1}{\sin C}, \)
where µ is the refractive index of diamond with respect to liquid.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Refractive index of diamond w.r.t. liquid
\({ }^{d} \mu_{l}=\frac{1}{\sin C}=\frac{\mu_{d}}{\mu_{l}} \Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{\sin C}\)
sin C = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) sin 45°
∴C = 45°
Question 8.
Assertion: Light travels faster in glass than in air.
Reason: Glass is denser than air.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is True
Explanation:
Light travels faster in air than in glass, because glass is denser than air.
Case-Based MCQs
Attempt any 4 sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
I. Following figure illustrates the ray diagram for the formation of image by a concave mirror. The position of the object is beyond the centre of curvature of the concave mirror. On the basis of given diagram answer any four questions from
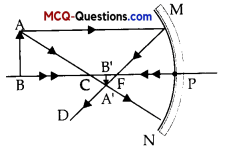
Question 1.
If the focal length of the concave mirror is 10 cm, the image formed will be at a distance .
(A) Between 10cm and 15cm
(B) Between 10cm and 20cm
(C) Beyond 20cm
(D) At 20 cm
Answer:
(B) Between 10cm and 20cm
Explanation:
If the focal length of the concave mirror is 10 cm, the image formed will be at a distance between 10 cm and 15 cm.
Question 2.
In case of concave mirror, the image distance is………. when image is formed in front of the mirror and………..when the image is formed behind the mirror.
(A) positive, negative
(B) negative, negative
(C) negative, positive
(D) positive, positive
Answer:
(C) negative, positive
Explanation:
If an image formed behind the concave mirror, the object distance is positive but if an image is formed in front of the mirror, the image distance is negative.
Question 3.
If the size of the object in the given figure is 5 cm and the magnification produced is -0.5. The size of the image is (in cm)…………..
(A) -2.5
(B) -0.1
(C) 2.5
(D) 0.1
Answer:
(A) -2.5
Explanation:
As we know, magnification,
m=\(\frac{h_{2}}{h_{1}} \)
h2 = \(\frac{-(0.5 \times 5)}{10}\)
h2 = -2.5
![]()
Question 4.
A negative sign in the magnification value indicate that the image is……….
(A) Real and inverted
(B) Real and erect
(C) Virtual and erect
(D) Virtual and inverted
Answer:
(A) Real and inverted
Explanation:
A negative sign in the magnification value indicate that the image is real and inverted.
Question 5.
An image formed by concave mirror is virtual, when the object is placed:
(A) at infinity
(B) at C
(C) Between C and F
(D) Between P and F
Answer:
(D) Between P and F
Explanation:
An image formed by concave mirror is virtual, when the object is placed between P and F.
II. Read the following passage and answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of the school laboratory by using a mirror.
Question 1.
Which type of mirror should he use and why ?
(A) Convex mirror, it forms virtual image
(B) Concave mirror, it forms virtual image
(C) Concave mirror, it forms real image
(D) Convex mirror, it forms real image
Answer:
(C) Concave mirror, it forms real image
Explanation:
He should use a concave mirror as it forms real images.
Question 2.
At what distance, in terms of focal length of the mirror, should he place the candle flame to get the magnified image on the wall ? Q;
(A) At F
(B) Between F and C
(C) At C
(D) At infinity
Answer:
(B) Between F and C
Explanation:
He should place the candle flame between the focus and centre of curvature of the mirror to get the magnified image on the wall.
Question 3.
To get the diminished image of the candle flame, the object must be placed at:
(A) infinity
(B) at C
(C) between F and C
(D) At F
Answer:
(A) infinity
Explanation:
To get the diminished image of the candle flame, the object must be placed at infinity.
![]()
Question 4.
If the image formed by this mirror is inverted and real, the magnification will be: A
(A) Positive
(B) Negative
(C) Either of them
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Negative
Explanation:
If the image formed by this mirror is inverted and real, the magnification will be negative.
Question 5.
A virtual image formed by concave mirror is:
(A) erect and enlarged
(B) erect and diminished
(C) inverted and diminished
(D) inverted and enlarged
Answer:
(A) erect and enlarged
Explanation:
A virtual image formed by concave mirror is erect and enlarged.
III. Read the following passage and answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 60 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 15 cm from its pole.
Question 1.
Suggest the type of mirror he should use:
(A) convex mirror
(B) plane mirror
(C) concave mirror
(D) none of the above
Answer:
(C) concave mirror
Explanation:
He should use a concave mirror, as it forms a real image on the same side of the mirror.
Question 2.
Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(A) – 4
(B) + 4
(C) – 900
(D) + 900
Answer:
(A) – 4
Explanation:
Object distance, u = -15 cm
Image distance, v = – 60 cm
Magnification, m = \(\frac{-v}{u}=\frac{-(-60)}{(-15)}=-4 \)
The minus sign in magnification shows that the image formed is real and inverted.
![]()
Question 3.
When object distance is less than focal length the image is and when object distance is more than focal length the image is .
(A) real in both case
(B) virtual in both case
(C) real, virtual
(D) virtual, real
Answer:
(D) virtual, real
Explanation:
When object distance is less than focal length the image is virtual and when object distance is more than focal length the image is real.
Question 4.
What is the distance between the object and its image ?
(A) 45 cm
(B) 35 cm
(C) 75 cm
(D) 0 cm
Answer:
(A) 45 cm
Explanation:
The image is formed at a distance of 45 cm from the object.
Question 5.
The image formed in the above case is:
(A) virtual, inverted and magnified.
(B) real, erect and magnified
(C) real, inverted and magnified
(D) real, erect and diminished
Answer:
(C) real, inverted and magnified
Explanation:
In this case, the image is formed beyond the centre of curvature. This image is real, inverted and enlarged.
IV Read the following passage and answer the following questions from Question 1. to Question 4.
A student focuses the image of a candle flame, placed at about 2 m from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm, on a screen. After that he moves gradually the flame towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen.
Question 1.
In which direction does he move the lens to focus the flame on the screen ?
(A) away from screen
(B) towards the screen
(C) should not move the screen
(D) toward the candle
Answer:
(D) toward the candle
Explanation:
Let us assume the screen to lens distance is greater than 20 cm. Since it is required to get image beyond 2F, the object should be F and 2F on other side of the lens. Hence student will move the lens towards candle. (F means a location at a distance from lens that equals the focal length of lens. 2F means distance that equals twice the focal length).
Question 2.
What happens to the size of the image of the flame formed on the screen?
(A) size of image will decrease
(B) size of image will increase
(C) remains unchanged
(D) size will become too small
Answer:
(B) size of image will increase
Explanation:
Size of the image of the flame increases when object is moving towards lens, from a distance beyond 2F, then 2F, then less than 2F.
![]()
Question 3.
What difference is seen in the intensity (brightness) of the image of the flame on the screen ?
(A) intensity of image increases
(B) intensity of image remains same
(C) intensity of image reduces
(D) the image disappears
Answer:
(A) intensity of image increases
Explanation:
As the object (candle) is moved towards lens more light intensity is collected by lens, hence brightness of the image increase.
Question 4.
What is seen on the screen when the flame is very close (at about 5 cm) to the lens ?
(A) a bright image
(B) a magnified image
(C) diminished image
(D) no image
Answer:
(D) no image
Explanation:
When the candle is very close about 5 cm, focussing the flame is not possible. Hence student will not get any image on the screen.
He will get diffused light on the screen.
V. Read the passage and note the following observations. Answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
A student focussed the image of a candle flame on a white screen by placing the flame at various distances from a convex lens. He noted his
| Distance of flame from the lens (cm) | Distance of the screen from the lens (cm) |
| (A) 60 | 20 |
| (B) 40 | 24 |
| (C) 30 | 30 |
| (D) 24 | 40 |
| (E) 15 | 70 |
Question 1.
From the above table, find the focal length of lens without using lens formula: |AEI
(A) 15cm
(B) 30cm
(C) 40cm
(D) 60cm
Answer:
(A) 15cm
Explanation:
u = 30 cm, v = 30 cm This is possible if the object is placed at 2f ∴ 2f = 30 cm, f= 15 cm
Question 2.
Which set of observations is incorrect?
(A) (a)
(B) (c)
(C) (e)
(D) (d)
Answer:
(C) (e)
Explanation:
u = 15 cm, v = 70 cm is incorrect. This is because if the object is at focus then image is formed at infinity.
![]()
Question 3.
In which case, the size of the object and image will be same:
(A) In (D) case
(B) In (B) case
(C) In (C) case
(D) In (A) case
Answer:
(C) In (C) case
Explanation:
In (C) case, because object is at the centre of curvature.
Question 4.
What is the change in image observed as the object is moved from infinity towards the concave lens?
(A) Size of image decreases
(B) Size of image becomes highly diminished
(C) Size of the image remains unchanged
(D) Size of the image increases slightly
Answer:
(D) Size of the image increases slightly
Explanation:
The size of the image increases slightly, though it remains diminished in comparison to the size of the object.
Question 5.
Which of the following statement is false for the formation of images by convex lens?
(A) It forms real,inverted and diminished image.
(B) It forms virtual erect and enlarged image.
(C) It forms virtual, erect, and diminished image.
(D) It forms real,inverted and enlarged image.
Answer:
(C) It forms virtual, erect, and diminished image.
Explanation:
Image formed by a convex mirror is always diminished and erect.
VI. Study the given diagram and answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
A very thin narrow beam of white light is made incident on three glass objects shown below.
Study the nature and behaviour of the emergent beam in all the three cases.

Question 1.
Following are the possibility of two emergent beams being similar. Choose the correct answer:
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) No similar emergent beams
Answer:
(B) (i) and (iii)
Explanation:
In (i) emergent beam is white and laterally displaced. In (ii) emergent beam is a spectrum of seven colours bent in different angles. In (iii) emergent beam from the second prism is white only. Similarity between (i) and (iii) as both emergent rays are white in colour
![]()
Question 2.
When light enters from air to glass, the angles of incidence and refraction in air and glass are 45° and 30°, respectively. Find the refractive index of glass.
\(\text { (Given that } \sin 45^{\circ}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} ; \sin 30^{\circ}=\frac{1}{2} \text { ) } \)
(A) √2
(B) 2√2
(C) 1/(√2)
(D) 1
Answer:
(A) √2
Explanation:
\(a_{g}=\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\frac{\sin 45^{\circ}}{\sin 30^{\circ}} \)
\(=\frac{\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}{\frac{1}{2}}=\sqrt{2} \)
Question 3.
The light changes its path as its medium changes. Which of the following is an incorrect statement ?
(A) Speed of light is different in different media.
(B) Light changes its path because light only travels in straight line.
(C) Speed of light is dependent on medium through which it is passing.
(D) The light chooses the path with minimum time, as it changes its medium.
Answer:
(B) Light changes its path because light only travels in straight line.
Explanation:
Speed of light is different in different media. As the medium changes, the light has to choose a path of minimum time. Hence, the direction of the light changes. This phenomenon is known as refraction of light.
Question 4.
What is the unit of refractive index? R
(A) Pascal
(B) Joule
(C) No unit
(D) p m
Answer:
(C) No unit
Explanation:
Refractive index being a ratio of two similar quantities hence has no unit.
![]()
Question 5.
Light travel fastest in:
(A) Air
(B) Vacuum
(C) Glass
(D) diamond
Answer:
(B) Vacuum
Explanation:
Light waves travel fastest through a vacuum and air, and slower through other materials such as glass or water.