Heredity and Evolution Class 10 MCQ Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(A) For every hormone there is a gene.
(B) For every protein there is a gene.
(C) For production of every enzyme there is a gene.
(D) For every molecule of fat there is a gene.
Answer:
(D) For every molecule of fat there is a gene.
Explanation:
Hormone and enzymes are proteins and formation of any particular protein is controlled by a particular gene. Hence, all other options are correct.
![]()
Question 2.
If a round, green seeded pea plant (RRyy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rrYY) the seeds produced in F, generation are
(A) round and yellow.
(B) round and green.
(C) wrinkled and green.
(D) wrinkled and yellow.
Answer:
(A) round and yellow.
Explanation:
As roundness and yellow colour are shown by capital letters in the genotype, so they are dominant traits. In FI generation, only dominant traits are expressed.
Question 3.
The maleness of a child is determined by
(A)the X chromosome in the zygote.
(B) the Y chromosome in zygote.
(C) the cytoplasm of germ cell which determines the sex.
(D) sex is determined by chance.
Answer:
(B) the Y chromosome in zygote.
Explanation:
Y-chromosome in zygote means that the zygote would develop into a male I j child.
Question 4.
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a
(A) boy.
(B) girl.
(C) X- chromosome does not determine the sex of a child.
(D) either boy or girl.
Answer:
(B) girl.
Explanation:
A zygote with XX chromosomes in the 23rd pair would develop into a girl child.
![]()
Question 5.
From the list given below, select the character which can be acquired but not inherited.
(A) colour of eye.
(B) colour of skin.
(C) size of body.
(D) nature of hair.
Answer:
(C) size of body.
Explanation:
Traits in other options are always inheritable traits.
Question 6.
Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be
(A) double fertilisation.
(B) self-pollination.
(C) cross fertilisation.
(D) no fertilization.
Answer:
(C) cross fertilisation.
Explanation:
As it is mentioned in the question that two pink coloured flowers were crossed, thus it is cross fertilization.
Question 7.
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
(A) tallness is the dominant trait.
(B) shortness is the dominant trait.
(C) tallness is the recessive trait.
(D) height of pea plant is not governed by gene’T’ oi’t’.
Answer:
(A) tallness is the dominant trait.
Explanation:
This is a case of monohybrid cross, in which all the progenies in the FI generation show dominant character. Hence, tallness is the dominant trait.
Question 8.
The number of pair (s) of sex chromosomes in the zygote of humans is
(A) one.
(B) two.
(C) three.
(D) four.
Answer:
(A) one.
Explanation:
The sex chromosomes are in the 23rd pair.
Question 9.
In evolutionary terms, we have more in common with
(A) a Chinese school-boy.
(B) a chimpanzee.
(C) a spider.
(D) a bacterium.
Answer:
(A) a Chinese school-boy.
Explanation:
In evolutionary terms, we have more in common with a Chinese school boy as both are humans and belong to same species.
![]()
Question 10.
The theory of evolution of species by natural selection was given by
(A) Mendel
(B) Darwin
(C) Morgan
(D) Lamarck
Answer:
(B) Darwin
Explanation:
The theory of evolution of species by natural selection was given by Charles Darwin.
Question 11.
The theory of inheritance of acquired characters was given by
(A) Mendel
(B) Darwin
(C) Morgan
(D) Lamarck
Answer:
(D) Lamarck
Explanation:
The theory of inheritance of acquired characters was given by Lamarck.
Question 12.
If the fossil of an organism is found in the deeper layers of earth, then we can predict that
(A) the extinction of organism has occurred recently.
(B) the extinction of organism has occurred thousands of years ago.
(C) the fossil position in the layers of earth is not related to its time of extinction.
(D) time of extinction cannot be determined.
Answer:
(B) the extinction of organism has occurred thousands of years ago.
Explanation:
Newer fossils are deposited in layers above older fossils.
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion: A geneticist crossed a pea plant having violet flowers with a pea plant having white flowers, he got all violet flowers in first generation. Reason: White colour gene is not passed on to next generation.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation: The gene for violet flowers is dominant over the gene for white flowers so that only the violet gene is expressed as violet flowers in the first generation.
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Mendel chose a number of varieties of garden pea as plant material for his experiments.
Reason (R): Garden pea has well defined characters and is bisexual.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Mendel chose garden pea as plant material for his experiment because garden pea plants were easily available they grow in one season fertilization was easy.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): In humans, males play an important role in determining the sex of the child.
Reason (R): Males have two X chromosomes.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Sex of a child is dependent on the type of the male gamete that fuses with the female gamete. Human beings possess 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of these, 22 pairs are known as autosomes, while the remaining one pair comprises sex chromosomes (XX in females and XY in males). At the time of fertilisation, the egg cell fuses with the sperm cell, resulting in the formation of the zygote. If the egg cell carrying an X chromosome fuses with the sperm carrying an X chromosome, the resulting child would be a girl. If the egg cell carrying an X chromosome fuses with the sperm carrying a Y chromosome, the resulting child would be a boy.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Learning a skill such as dance and music is an acquired trait.
Reason (R): Acquired traits develop in the life time of an individual and do not pass to the progeny.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Trails which develop in the life time of an individual and do not pass to the progeny are called acquired traits. Learning a skill such as dance/music/loss of body parts/’ weight etc are example of acquired traits.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Traits like eye colour or height are inherited traits.
Reason (R): Inherited traits are not transferred from parents to young ones.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Eye colour and height are genetically inherited traits, as these are expressed by genes. Inherited traits are the traits which are transferred from parents to young ones. Acquired traits are the characters that are acquired by the individual during its lifetime. These traits cannot be inherited. For example, if a wrestler develops large muscles due to his training program that does not mean it will be passed on to his offspring.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Fossils are remains of dead organisms.
Reason (R): It is helpful in study of evolution.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Fossils are remains of hard parts of the dead organisms in the strata of earth. It help in tracing evolutionary pathways.
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Wings of butterfly and wings of bat are analogous orgAnswer:
Reason (R): Analogous organs have different origin and structural plan but same function.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Wings of butterfly and wings of bat though they perform similar function, they have different origin/basic structure. Hence, they are known as analogous orgAnswer:
![]()
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Speciation is the process of formation of a new species from a pre-existing one.
Reason (R): Mutation plays a role in speciation.
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation:
Speciation is an evolutionary process by which new species arise. One of the factors that lead to speciation is mutation.
Question 9.
Assertion (A): Natural selection is the phenomenon by which the nature selects those species which possess survival advantage over the other species.
Reason (R): According to theory of natural selection, there is struggle of existence within the species of a population for the environmental resources and their struggle leads to survival of certain organisms and elimination of the less competent species.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Natural selection is the phenomenon by which the nature selects those species which possess survival advantage over the other species. According to theory of natural selection, there is struggle of existence within the species of a population for the environmental resources and their struggle leads to survival of certain organisms and elimination of the less competent species.
Case-Based MCQs
Attempt any 4 sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
I. Read the passage and answer the following questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
In a cross between plants with purple flowers and plants with white flowers, the offspring of Fj generation all had white flowers. When the Fj generation was self-crossed, it was observed in the F2 generation that out of 100, 75 flowers were white. Make a cross and answer the following questions:

Question 1.
The above cross is known as:
(A) Monohybrid cross
(B) Dihybrid cross
(C) Test cross
(D) Back cross
Answer:
(A) Monohybrid cross
Explanation:
A cross between two plants, which differ in only one pair of contrasting characters is calld monohybrid cross. In this cross, F2 phenotypic ratio is 3 :1 and genotypic ratio is 1: 2 :1.
Question 2.
In a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals, percentage of pure homozygous individuals obtained in F1 generation is ?
(A) 25%
(B) 50%
(C) 75%
(D) 100%
Answer:
(B) 50%
Explanation:
In a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals, percentage of pure homozygous individuals obtained in F, generation is 50 %.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of these is not the genotype of F progeny?
(A) WW
(B) Ww
(C) ww
(D) Wp
Answer:
(D) Wp
Explanation:
Genotypes of F2 progeny are WW, Ww, ww.
Question 4.
The ratio of ‘White: Purple’ flowers in the F2 generation is
(A) 3:1
(B) 1: 2
(C) 1 : 3
(D) 2 :1
Answer:
(A) 3:1
Explanation:
Ratio between White : Purple flowers are 3:1.
II. Study the given cross showing self pollination in F1 and answer the following questions from Question 1. to Question 4.
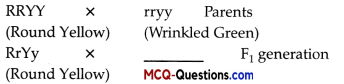
Question 1.
The missing blank in the above cross is:
(A) RrYy
(B) RRYY
(C) RryY
(D) rryy
Answer:
(A) RrYy
Explanation:
RrYy (Round Yellow) is the I missing blank in the above cross.
Question 2.
The combination of characters in the F2 progeny are:
(A) Round Yellow: Round Green: Wrinkled Yellow: Wrinkled Green
(B) Round Green : Round Yellow : Wrinkled yellow : Wrinkled Green
(C) Round Yellow : Round Green : Wrinkled Green: Wrinkled yellow
(D) Round Green : Round Yellow : Wrinkled yellow : Wrinkled Green
Answer:
(A) Round Yellow: Round Green: Wrinkled Yellow: Wrinkled Green
Explanation:
In F2 generation, the combination of characters is Round Yellow: Round Green: Wrinkled yellow: Wrinkled Green.
Question 3.
The ratio of the combination of characters in the F2 progeny is:
(A) 3: 1
(B) 1: 2: 1
(C) 1 1: 1
(D) 9 : 3 : 3 :1
Answer:
(D) 9 : 3 : 3 :1
Explanation:
The ratio of the combination of 8 characters in the F2 progeny is 9: 3: 3:1.
![]()
Question 4.
A Mendelian experiment consists of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent cod depicted as
(A) TTWW
(B) TTww
(C) TtWW
(D) TtWw
Answer:
(C) TtWW
Explanation:
All progeny bore violet flower, so they all must have gene for violet flower. As violet colour appears in hybrids thus it must be the dominant character. So, white flowered plant should have ww genes to show recessive white character. It indicates that all progenies got allele W (violet colour) from tall-violet flowered plant, thus its all gametes should have this allele. To serve the purpose plant must have WW genes. But, tallness was found in 50% progenies thus half of its gametes contained T gene and other half contained t gene. Inclusively, the tall plant had TtWW genotype.
III. Read the given passage and answer any of the four questions from Question 1. to Question 5. given below:
Seema crossed pure breed pea plants having round-yellow seeds with wrinkled green seeds and found that only A-B type of seeds were produced in the F, generation. When F, generation pea plants having A-B type of seeds were cross-breed by self pollination, then in addition to the original round yellow and wrinkled green seeds, two new varieties A-D and C-B types of seeds were also obtained.
Question 1.
What are A-B type of seeds?
(A) Round -yellow
(B) Round- green
(C) Wrinkled-yellow
(D) Wrinkled-green
Answer:
(A) Round -yellow
Explanation:
A-B type of seeds are round in shape and yellow in colour.
Question 2.
A and B are……… traits.
(A) dominant
(B) recessive
Answer:
(A) dominant
Explanation:
A-B type is dominant traits.
Question 3.
A-D are……… and C-B are ……….. type of seeds.
(A) Round green and wrinkled yellow respectively
(B) Round yellow and wrinkled green respectively
(C) Wrinkled green and round green respectively
(D) Wrinkled green and round yellow respectively
Answer:
(A) Round green and wrinkled yellow respectively
Explanation:
A-D is round-green while C-B is wrinkled- yellow.
![]()
Question 4.
Which one of these will be produced in minimum and maximum number in the F2 generation?
(A) A-B
(B) A-D
Answer:
(A) A-B
Explanation:
A-B is produced in maximum number while A-D will be produced in minimum number.
![]()
Question 5.
The above cross is known as
(A) Monohybrid cross
(B) Dihybrid cross
(C) Test cross
(D) Back cross
Answer:
(B) Dihybrid cross
Explanation:
A cross between two plants, which differ in two pairs of contrasting characters are called dihybrid cross.