MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 MCQ Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field :
(A) The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points.
(B) Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
(C) If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength.
(D) Relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines. JJ
Answer:
(C) If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength.
Explanation:
Magnetic field lines appear parallel when they are far from the magnet. But this does not mean that field strength is zero. No field line would be present where field strength becomes zero.
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight current carrying wire?
(A) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(B) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(C) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(D) The field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire.
Answer:
(D) The field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire.
Explanation:
The field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire. On applying right-hand thumb rule, we find the direction of magnetic field. The field is in the form of concentric circles centered on the wire carrying current.
![]()
Question 3.
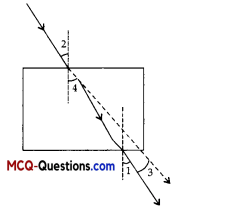
A constant current flowing in a horizontal wire in the plane of the paper from East to West is shown in Figure. The direction of magnetic field at a point will be from North to South :

(A) directly above the wire.
(B) directly below the wire.
(C) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the north side of the wire.
(D) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the south side of the wire.
Answer:
(B) directly below the wire.
Explanation:
Line WE shows a straight conductor through which current is moving from E to W. When seen from east, the magnetic field lines appear in clockwise direction, i.e. S to N above the wire and N to S below the wire. This is in accordance with right hand thumb rule.
Question 4.
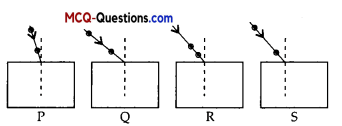
If the key in the arrangement in the given Figure, is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are:

(A) concentric circles.
(B) lliptical in shape.
(C) straight lines parallel to each other.
(D) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it.
Answer:
(C) straight lines parallel to each other.
Explanation:
When the key is taken out, the circuit is open, no current flows and no magnetic field due to current carrying conductor. There exists only earth’s magnetic field which will exhibit straight lines parallel to each other.
Question 5.
For a current in a long straight solenoid N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is :
(A) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
(B) The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the coil.
(C) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
(D) The N and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Answer:
(C) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
Explanation: A solenoid behaves like a bar magnet. Hence, the pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is same as the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
![]()
Question 6.
The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is :
(A) more at the ends than at the centre
(B) minimum in the middle
(C) same at all points
(D) found to increase from one end to the other
Answer:
(C) same at all points
Explanation:
Magnetic field lines are straight and parallel inside the solenoid. This indicates a same magnetic field. Hence, inside the solenoid, the magnetic field is same throughout.
Question 7.
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
(A) Mass
(B) Speed
(C) Velocity
(D) Momentum
Answer:
(C) Velocity (D) Momentum
Explanation:
When a proton enters a magnetic field, it starts moving on a circular path. Because of its movement along a circular path it attains angular momentum. We know that momentum is a product of mass and velocity. Therefore velocity and mass of a proton change when it enters a magnetic field.
Question 8.
A positively-charged particle (alpha – particle pro-jected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is
(A) towards south.
(B) towards east.
(C) downward.
(D) upward.
Answer:
(D) upward.
Explanation:
In accordance with Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, the direction of magnetic field is vertically upward.
Question 9.
The phenomenon of electro-magnetic induction is :
(A) the process of charging a body.
(B) the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
(C) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
(D) the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
Answer:
(C) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
Explanation: In electro-magnetic induction phenomenon, an induced current begins to flow in a coil whenever there is a change in magnetic field in and around a coil.
Question 10.
The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that:
(A) AC generator has an electro-magnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
(B) DC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(C) AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(D) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Answer:
(D) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Explanation:
AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
![]()
Question 11.
Choose the correct option. A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each:
(A) two revolutions.
(B) one revolution.
(C) half revolution.
(D) one-fourth revolution.
Answer:
(C) half revolution.
Explanation:
When a rectangular coil of copper wire is rotated in a magnetic field, the direction of the induced current changes once in each half revolution.
Question 12.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(A) Fleming’s right-hand rule is a simple rule to know the direction of induced current.
(B) The right-hand thumb rule is used to find the direction of magnetic fields due to current-carrying conductors.
(C) The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the direct current always flows in one direction, whereas the alternating current reverses its direction periodically.
(D) In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/50 second.
Answer:
(D) In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/50 second.
Explanation:
In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/100 second.
Question 13.
At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit:
(A) reduces substantially
(B) does not change
(C) increases heavily
(D) vary continuously
Answer:
(C) increases heavily
Explanation:
At the time of short circuiting the live wire and the neutral wire come into direct contact. As a result, the current in the circuit increases abruptly.
![]()
Question 14.
The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is :
(A) Earthing
(B) use of fuse
(C) use of stabilisers
(D) use of electric meter A
Answer:
(B) use of fuse
Explanation:
A fuse is a short length of wire designed to melt in the event of excessive current flow.
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Two bar magnets attract when they are brought near to each other with the same pole.
Reason (R): Unlike poles will attract each other.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Two bar magnets repel when same poles face each other. Opposite poles attract each other
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Magnetic field lines never intersect.
Reason (R): At a particular point magnetic field has only one direction.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Magnetic field lines never intersect each other as for two lines to intersect, there must be two north directions at a point, which is not possible.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): In Fleming’s Left Hand Rule, the direction of magnetic field, force and current are mutually perpendicular.
Reason (R): Fleming’s Left hand Rule is applied to measure the induced current.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
It is used to find the direction of force in a current carrying conductor in the presence of magnetic field.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): An alpha particle placed in a magnetic field will not experience any force, if it moves in the magnetic field parallel to field lines.
Reason (R): The force is zero if current and field are in the same direction.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
An alpha particle placed in a magnetic field will not experience any force, if it moves in the magnetic field parallel to field lines. It is because, the force is zero if current and field is in the same direction.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Safety fuses are made up of materials having a low melting point.
Reason (R): Safety fuses should be resistant to electric current.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Safety fuses are made up of materials having a low melting point so that when excess current flow through the circuit,
the fuse melts breaking the circuit and thus prevents appliances.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Copper is used to make electric wires.
Reason (R): Copper has very low electrical resistance.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
The low electrical resistance of copper makes it a good conductor for electricity.
![]()
Question 7.
Assertion (A): When two bulbs are operated on same voltage supply, having power 60 W and 100 W then 100 W bulb has less resistance than 60 W. Reason (R): The power of the bulb is directly proportional to the square of the voltage.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Since, power (P) Hence, 100 W bulb has less resistance.
Case-Based MCQs
Attempt any 4 sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
I. Read the following passage and answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
A solenoid is a long helical coil of wire through which a current is run in order to create a magnetic field. The magnetic field of the solenoid is the superposition of the fields due to the current through each coil. It is nearly uniform inside the solenoid and close to zero outside and is similar to the field of a bar magnet having a north pole at one end and a south pole at the other depending upon the direction of current flow.
The magnetic field produced in the solenoid is dependent on a few factors such as, the current in the coil, number of turns per unit length etc. The following graph is obtained by a researcher while doing an experiment to see the variation of the magnetic field with respect to the current in the solenoid.
The unit of magnetic field as given in the graph attached is in mili-Tesla (mT) and the current is given in Ampere.

Question 1.
What type of energy conversion is observed in a linear solenoid?
(A) Mechanical to Magnetic
(B) Electrical to Magnetic
(C) Electrical to Mechanical
(D) Magnetic to Mechanical
Answer:
(B) Electrical to Magnetic
Explanation:
In a solenoid, the current flowing through the circuit generates its own magnetic field. Hence the electrical energy of the circuit is converted to magnetic field.
![]()
Question 2.
What will happen if a soft iron bar is placed inside the solenoid?
(A) The bar will be electrocuted resulting in short- circuit.
(B) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
(C) The bar will be magnetised permanently.
(D) The bar will not be affected by any meAnswer:
Answer:
(B) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
Explanation:
The magnetic field produced by the solenoid will be reinforced by the iron bar and it will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
Question 3.
The magnetic field lines produced inside the solenoid are similar to that of… A
(A) a bar magnet
(B) a straight current carrying conductor
(C) a circular current carrying loop
(D) electromagnet of any shape
Answer:
(A) a bar magnet
Explanation:
Solenoids mimic bar magnets. The magnetic field of a solenoid are similar to that of a bar magnet and just like a bar magnet a solenoid also has north and south poles.
Question 4.
After analysing the graph a student writes the following statements.
(A) The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is inversely proportional to the current.
(B) The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to the current.
(C) The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to square of the current.
(D) The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is independent of the current. Choose from the following which of the following would be the correct statement(s).
(A) Only IV
(B) I and III and IV
(C) I and II
(D) Only II
Answer:
(D) Only II
Explanation:
As can be seen from the graph the magnetic field is increasing linearly with current. Therefore, the current is directly proportional to the magnetic field.
Question 5.
From the graph deduce which of the following statements is correct ?
(A) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 13 mT
(B) For larger currents, the magnetic field increases non-linearly.
(C) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 1.3 mT
(D) There is not enough information to find the magnetic field corresponding to 0.8A current.
Answer:
(A) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 13 mT
Explanation:
From the above graph we can see that 0.8 A corresponds to 13 mT magnetic field.
II. Study the given diagram and answer any of the four questions form Question 1. to Question 5.
In the given diagram, two coils of insulated copper wire are wound over a nonconducting cylinder as shown. Coil P has larger number of turns.

Question 1.
A momentary deflection is shown by the galvanometer, when:
(A) Key K is open
(B) Key K is closed
(C) In both the situations
(D) In neither of the case.
Answer:
(C) In both the situations
Explanation:
Momentary deflection is seen in both the cases. When the key K is open, deflection is shown by the galvanometer and when it is closed, a momentary deflection is seen in opposite direction.
![]()
Question 2.
Which phenomenon is involved in it ?
(A) Electromagnetic induction
(B) Magnetism
(C) Electromagnetism
(D) None of these
Answer:
(A) Electromagnetic induction
Explanation:
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field in a conductor induces current in another conductor.
Question 3.
In above phenomenon, the current is induced in another conductor,
(A) By changing magnetic field
(B) By increasing the strength of current
(C) By decreasing the strength of the current
(D) By using extra wire.
Answer:
(A) By changing magnetic field
Explanation:
Electromagnetic current is induced in another conductor by changing the magnetic field.
Question 4.
The rule which helps us to know direction of induced current:
(A) Flemings right hand rule
(B) Flemings left hand rule
(C) Electro magnetic induction
(D) Faraday’s Law
Answer:
(A) Flemings right hand rule
Explanation:
Flemings right hand rule helps us to know the direction of induced current.
Question 5.
Flemings right hand rule explains:
(A) Direction of magnetic field
(B) Direction of motion of conductor
(C) Only (a)
(D) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(D) Both (a) and (b)
Explanation:
In Fleming’s Right Hand Rule the first three fingers of the right hand are mutually perpendicular to each other such that the forefinger gives the direction of magnetic field and the thumb points in the direction of the motion of a conductor then, the middle finger will give the direction of the induced current.
![]()
III. Read the following passage and answer any four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.
A student fixes a sheet of white paper on a drawing board. He places a bar magnet in the centre of it. He sprinkles some iron filings uniformly around the bar magnet. Then he taps the board gently and observes that the iron filings arrange themselves in a particular pattern.
Question 1.
Why do the iron fillings arrange themselves in a particular pattern ?
(A) Due to external force applied on the magnet.
(B) Due to force exerted by the magnet outside the magnetic field.
(C) Due to the force exerted by magnet within its magnetic field.
(D) Due to pressure of magnetic field.
Answer:
(C) Due to the force exerted by magnet within its magnetic field.
Explanation:
It is due to the force exerted by the magnet within its magnetic field.
Question 2.
What do the lines along which the iron fillings align represent ?
(A) North pole and south pole of the magnet
(B) Strength of the magnet
(C) Magnetic field lines
(D) Gravitational force.
Answer:
(C) Magnetic field lines
Explanation:
The lines represent magnetic field lines.
Question 3.
What does the crowding of iron filings at the end of the magnet indicate?
(A) Magnetic field is strongest near the poles of the magnet.
(B) Magnetic field is weakest near the poles of the magnet.
(C) There is no significant magnetic field at the poles of the magnet.
(D) The significance of polarity
Answer:
(A) Magnetic field is strongest near the poles of the magnet.
Explanation:
Crowding of iron filings at the ends of the magnet indicates that the magnetic field is strongest near the poles of the magnet.
![]()
Question 4.
The closer field lines indicate:
(A) Magnetic field in that region is weak
(B) Magnetic field in that region is strong.
(C) Magnetic field in that region is zero.
(D) North and South poles are closer.
Answer:
(B) Magnetic field in that region is strong.
Explanation:
The strength of magnetic field is indicated by the closeness of the field lines. Closer the lines, more will be the strength and farther the lines, lesser will be the field strength.
Question 5.
What is SI unit of magnetic field:
(A) Pascal
(B) Nm2
(C) Tesla
(D) No unit
Answer:
(C) Tesla
Explanation:
Tesla is the SI unit of magnetic field.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Read More »