Life Processes Class 10 MCQ Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect?
(A) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
(B) They store carbohydrates in the form of starch.
(C) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight.
(D) They constitute the first trophic level in food chains
Answer:
(C) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight.
Explanation:
Autotrophs take in food from the outside world and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide and water which is converted into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.

Question 2.
In which of the following groups of organisms, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed?
(A) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(B) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(C) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(D) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm W
Answer:
(B) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Explanation:
These are saprotrophs and digestion in saprotrophs take place before ingestion. They break down and convert complex organic molecules present in dead and decaying matter into simpler substances outside their body.
Question 3.
Which is the correct sequence of parts in human alimentary canal?
(A) Mouth → stomach → small intestine → oesophagus → large intestine
(B) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → large intestine → small intestine
(C) Mouth → stomach → oesophagus → small intestine → large intestine
(D) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
Answer:
(D) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
Explanation:
The sequence of organs in human alimentary canal are: Mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus.

Question 4.
If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(A) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(B) Starch breaking down into sugars
(C) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(D) Absorption of vitamins
Answer:
(B) Starch breaking down into sugars
Explanation:
If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, the process of starch digestion will get disturb as salivary amylase helps in digestion of starch.
Question 5.
Select the correct statement.
(A) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food.
(B) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis.
(C) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food.
(D) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates.
Answer:
(A) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food.
Explanation:
Heterotrophs are organisms which cannot make their own food from inorganic substances like CO2 and water as they do not have chlorophyll to trap solar energy. They depend on other organisms for their food. Autotrophs synthesize their own food through photosynthesis by utilizing solar energy, e.g., green plants.
Question 6.
The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(A) carbon dioxide and water
(B) chlorophyll
(C) sunlight
(D) all of these
Answer:
(D) all of these
Explanation:
The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight.
Question 7.
The inner lining of stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid. Choose the correct one.
(A) Pepsin
(B) Mucus
(C) Salivary amylase
(D) Bile 5
Answer:
(B) Mucus
Explanation:
The stomach has a lining of mucus cells. The mucus is secreted in the gastric juice by the glands present in the stomach wall. It helps to protect the wall of stomach from its own secretions of hydrochloric acid. If mucus is not secreted, HCl will cause the erosion of inner lining of stomach leading to ulcer formation.

Question 8.
A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blue-black in colour. This indicates that rice water contains
(A) complex proteins
(B) simple proteins
(C) fats
(D) starch
Answer:
(D) starch
Explanation:
The formation of blue-black colour of rice water confirms the presence of starch. Starch forms a dark blue complex with iodine. When iodine is added it will show no colour change in case of proteins or fats.
Question 9.
The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
(A) cytoplasm
(B) mitochondria
(C) chloroplast
(D) nucleus
Answer:
(B) mitochondria
Explanation:
The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in mitochondria.
Question 10.
The correct sequence of anaerobic reactions in yeast is

Answer:

Explanation:
Yeast is an unicellular eukaryote which carries out ethanol fermentation. In the first phase, glucose is converted into pyruvate (glycolysis) in the cytoplasm of the cell. Due to limited oxygen availability, pyruvate remains in cytoplasm where pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes carry out the second phase of anaerobic respiration and produce ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Question 11.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast.
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria.
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria.
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration.
(A) (i) and (iii)
(B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (i) and (iv)
(D) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(C) (i) and (iv)
Explanation:
Yeast is a unicellular organism which brings out ethanol fermentation. The first stage is break down of one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate that occurs in cytoplasm. Because of limited oxygen availability, pyruvate remains in cytoplasm where pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes carry out the second phase of anaerobic respiration and produce ethanol and carbon dioxide.

Question 12.
During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(A) cytoplasm
(B) chloroplast
(C) mitochondria
(D) golgi body
Answer:
(A) cytoplasm
Explanation:
Lactic acid is formed after anaerobic respiration in muscle cells and this happens in cytoplasm.
Question 13.
Which of the following completes the given equation? Glucose + Oxygen (?)
(A) Only carbon dioxide + water + energy
(B) Only carbon dioxide + water
(C) Only carbon dioxide
(D) Only water + energy
Answer:
(A) Only carbon dioxide + water + energy
Explanation:
The given equation represents aerobic respiration. Glucose + oxygen -»carbon dioxide + water+ energy
Question 14.
Which of the following take place after we exercise?
(A) Out body needs more oxygen.
(B) Our body needs to replace the energy used.
(C) Our body needs to get rid of excess carbon dioxide.
(D) All of these 53
Answer:
(D) All of these 53
Explanation:
Our body needs more energy when we do exercise. We get energy by the oxidation of food. Due to exercise the body is able to get rid of excess carbon dioxide.

Question 15.
Which of these statements is correct about alveoli?
(A) They form a very large surface area.
(B) They have a very thin wall.
(C) They are covered with blood capillaries.
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Explanation:
Alveoli have a large surface area with very thin walls which is richly supplied with blood vessels and are always moist.
Question 16.
As air passes through the nasal cavity, it is
(A) Filtered in the nostrils
(B) Moistened by mucus
(C) Warmed to the body temperature
(D) Al of these
Answer:
(D) Al of these
Explanation:
Before air is breathed into the lungs, it is filtered in the nostrils, moistened by mucus and gets warmer equal to the body temperature.
Question 17.
What prevents back flow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(A) Valves in heart
(B) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(C) Thin walls of atria
(D) Al of the above
Answer:
(A) Valves in heart
Explanation:
Valves ensure that blood does not flow backwards when the atria or ventricles contract. Semilunar valves, the valves present between ventricles and their attached vessels, serve to prevent the backflow of blood to ventricles from their respective attached vessels. Likewise, atrioventricular (AV) valve between atrium and ventricle directs the flow of blood and prevents any backflow into atria.

Question 18.
Single circulation, i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by
(A) Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
(B) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
(C) Hyla, Ram, Draco
(D) Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
Answer:
(B) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
Explanation:
Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Ambas belong to class pisces. Fishes have two chambered heart and exhibit single circulation while three chambered heart of amphibians and reptiles and four chambered heart of birds and mammals exhibit double circulation.
Question 19.
The blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in
(A) carbon dioxide
(B) water
(C) haemoglobin
(D) oxygen 5
Answer:
(A) carbon dioxide
Explanation:
The anterior vena cava collects deoxygenated blood from the head, chest, and arms and enters the right atrium while the inferior vena cava collects blood from the lower body regions. Both venae cavae pass the deoxygenated blood to the right atrium. Therefore, blood from tissues is rich in carbon dioxide.
Question 20.
The xylem in plants are responsible for
(A) transport of water
(B) transport of food
(C) transport of amino acids
(D) transport of oxygen
Answer:
(A) transport of water
Explanation:
In a plant, the xylem is responsible for transport of water.

Question 21.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about heart?
(i) Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of body while right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from lungs.
(ii) Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs.
(iii) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to right ventricle which sends it to different body parts,
(iv) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body while left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body
(A) (i)
(B) (ii)
(C) (ii) and (iv)
(D) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(C) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation:
Blood from right atrium enters right ventricle and pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs for oxygenation.
Question 22.
In which of the following vertebrate group/ groups, heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
(A) Pisces and amphibians
(B) Amphibians and reptiles
(C)Amphibians only
(D) Pisces only
Answer:
(D) Pisces only
Explanation:
In fishes, heart sends the blood to gills from where blood is circulated to different orgAnswer:
Question 23.
Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
(A) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart.
(B) They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carry blood away from the heart to various organs of the body.
(C) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body.
(D) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
Answer:
(D) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
Explanation:
Arteries are the valveless blood vessels which serve to transport the blood away from the heart to various body parts. The thick strong elastic walls of arteries withstand the high pressure of blood coming from heart.
Question 24.
Which of these statements is correct about the function of blood?
(A) It helps in transportation of respiratory gases.
(B) It regulates body temperature.
(C) It helps in transportation of waste products.
(D) All the above
Answer:
(D) All the above
Explanation:
Blood has many different functions, like transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues, regulating body temperature, forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss, and carrying cells and antibodies that fight infection.

Question 25.
The filtration units of kidneys are called
(A) ureter
(B) urethra
(C) neurons
(D) nephrons
Answer:
(D) nephrons
Explanation:
Nephrons are the structural and functional unit of kidney that serve in filtration, reabsorption and secretion. Ureters are small muscular tubes that extend from the kidney and carry urine into the urinary bladder. The urethra is a canal that carries urine from bladder and expels it out of body. Neurons are structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Question 26.
The kidneys in human beings are a part of the sys-tem for
(A) nutrition
(B) respiration
(C) excretion
(D) transportation.
Answer:
(C) excretion
Explanation:
In human beings, the kidneys are a part of the system for excretion.
Question 27.
Match the words of Column (A) with that of Column (B)
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (A) Phloem | (i) Excretion |
| (B) Nephron | (ii) Translocation of food |
| (C) Veins | (iii) Clotting of blood |
| (D) Platelet | (iv) Deoxygenated blood |
(A) A – (ii), B – (i), C – (iv), D – (iii)
(B) A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (i), D – (iv)
(C) A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (ii), D – (i)
(D) A – (i), B – (iv), C – (iii), D – (iv)
Answer:
(A) A – (ii), B – (i), C – (iv), D – (iii)
Explanation:
S. No. Column
(A) Column
(B) Explanation
| S. No | Column (A) | Column (B) | Expianation |
| A | Phloem | (ii) | Phloem helps in translocation of food. |
| B | Nephron | (i) | Nephron helps in excretion. |
| C | Veins | (iv) | Veins carry deoxy-genated blood. |
| D | Platelets | (iii) | Platelets helps in clotting of blood. |
Question 28.
Which of the following is the structural and functional unit of the excretory system?
(A) Neuron
(B) Nephron
(C) Alveolus
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(B) Nephron
Explanation:
Nephron is the structural and functional unit of excretory system.

Question 29.
Choose the correct path of urine in our body :
(A) kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(B) kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(C) kidney → ureters —> urinary bladder →urethra
(D) urinary bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Answer:
(C) kidney → ureters —> urinary bladder →urethra
Explanation:
Kidneys are the paired organ where urine formation takes place. Small muscular tube, called as ureter, extend from kidneys and carry blood to urinary bladder. The urethra is a small tube that extends from the urinary bladder to an external opening.
Question 30.
Which of the following substances are removed from blood in the kidneys?
(A) Water
(B) Urea
(C) Sodium
(D) Ammonia
Answer:
(B) Urea
Explanation:
Urea is removed by the blood in kidneys by filtration.
Question 31.
Each nephron has a cup shaped upper end called…………… . which contains a………. .
(A) Bowman’s capsule, Ampulla
(B) Capillaries, Bowman’s capsule
(C) Ampulla, Glomerulus
(D) Bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus
Answer:
(D) Bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus
Explanation:
The upper cup shaped end of a nephron is called Bowman’s capsule. It contains glomerulus which is a group of blood capillaries.
Question 32.
Which of the following is used artificially to remove nitrogenous waste products from the blood?
(A) Ventilator
(B) Transfusion
(C) Hemodialysis
(D) Angiogram
Answer:
(C) Hemodialysis
Explanation:
Hemodialysis is used to remove nitrogenous waste products from the blood.

Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): HCl converts pepsinogen into active enzyme pepsin.
Reason (R): Pepsin converts protein into proteoses and peptones.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
HCl creates an acidic medium, which facilitates activation of pepsinogen into pepsin. The active enzyme pepsin converts proteins into proteoses and peptones.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Digestion breaks large complex molecules to simple smaller molecules which can be easily absorbed.
Reason (R): Digestion is necessary for the absorption of all molecules.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Digestion breaks large complex organic molecules to simple smaller ones which can be easily absorbed. However, certain molecules such as glucose, vitamin C etc, do not need any digestion before their absorption.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Muscles of stomach wall possess thick layers of muscle fibers.
Reason (R): These muscles help in mixing the food with the enzymes present in the alimentary canal.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
The lining of alimentary canal has muscles that contract rhythmically in order to push the food forward. This is known as peristaltic movement.

Question 4.
Assertion (A): Lipases help in emulsification of fats.
Reason (R): Lipases hydrolyses fats and oils.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Bile helps in emulsification of fats whereas lipases are the enzymes which hydrolyze fats and oils.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Photosynthesis is an anabolic process.
Reason (R): The process of photosynthesis occurs in chlorophyll.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Photosynthesis is an anabolic process as it takes C02 and H20 and then assembles them into glucose. The process of photosynthesis occurs in chloroplast.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Energy is used during the process of respiration.
Reason (R): Respiration stores energy in the form of ATP.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Respiration involves the oxidation of glucose inside the mitochondria to produce energy, which is stored in the high energy bonds of ATP molecules as biologically useful energy.
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Humans are not truly aerobic.
Reason (R): They produce lactic acid anaerobically.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Humans are aerobically respiring animals, but sometimes anaerobic respiration takes place in certain tissues like skeletal muscles, which do not get immediately as much oxygen as it requires. Therefore, the muscles respire anaerobically and produce lactic acid from glucose.

Question 8.
Assertion (A): In humans, there is a complex respiratory system.
Reason (R): Human skin is impermeable to gases.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Humans need more oxygen to maintain their high metabolic rates. Thus, a complex respiratory system has evolved so as to meet this need.
Question 9.
Assertion (A): Alveoli contain an extensive network of blood vessels.
Reason (R): Alveoli is the site where exchange of gases occurs.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
The alveoli of lungs are richly supplied with blood and are the sites where exchange of gases (O2 and CO2) occurs between blood and atmosphere.
Question 10.
Assertion (A): The muscular walls of ventricles are thicker than auricles.
Reason (R): This helps in preventing the back flow of blood.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Since ventricles have to pump blood into various organs, they have thicker muscular walls than atria do. Valves prevent back flow of blood.
Question 11.
Assertion (A): In human heart, there is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Reason (R): Valves are present in the heart which allows the movement of blood in one direction only.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood due to presence of inter-auricular and inter – ventricular septum. On the other hand, valves are present in the heart which allows the movement of blood in one direction only.

Question 12.
Assertion (A): Valves are present in the arteries.
Reason (R): Arteries carry oxygenated blood from heart to different body parts except pulmonary artery.
Answer:
(D) A is false and R is true.
Explanation:
Valves are absent in arteries, I whereas it is present in veins, which prevent back flow of blood.
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Plants have low energy needs.
Reason (R): Plant bodies have large proportion of dead cells.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Because plants have a large proportion of dead cells in many tissues. So, their energy needs are low and they can afford to have slow transport system.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): Human body produces highly toxic substances, which if not eliminated may cause the death.
Reason (R): Excretory substance removes nitrog-enous waste from the body.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
The biological process which involves the removal of harmful metabolic wastes from the body is called excretion. If these harmful wastes are not removed from the body, then it may cause the death of the organism.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Excretory unit of kidneys are nephrons.
Reason (R): It has no role in secretion of urine.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Nephrons are the basic filtration unit of kidneys. They carry out filtration, selective reabsorption and tubular secretion to from urine in kidneys, which is then passed out through the urethra, via the ureters and urinary bladder.

Question 15.
Assertion (A): Haemodialysis can save the life of patients with kidney failure.
Reason (R): Waste products like urea can be removed from the blood by haemodialysis.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
In case of kidney failure, haemodialysis is the process of purifying blood (or removing waste products like urea) by an artificial kidney. This can save the life of the patient.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): In humans, major amount of water is absorbed by the tubular part of nephron.
Reason (R): Absorption of water depends on the dissolved waste to be excreted from the body.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Major amount of water is selectively re-absorbed by the tubular part of nephron in humAnswer: It depends on the amount of excess water present in the body and dissolved waste to be excreted from the body.
Case-Based MCQs
Attempt any 4 sub-parts from each question. Each sub-part carries 1 mark.
I. Read the given passage and answer any of the four questions from Question l. to Question 5.
Sanjana is suffering from a frequent stomach pain and vomiting. She went to the Doctor. The doctor asked her to go for an ultrasound. In the report, a stone was found in her gall bladder. Doctor asked her to remove the gall bladder by operation. But she was reluctant to go for the operation.
Question 1.
The role played by gall bladder in human body is
(A) To store bile
(B) To secrete bile
(C) To emulsify fats
(D) To digest fats
Answer:
(A) To store bile
Explanation:
Gall bladder stores bile.
Question 2.
Removal of gall bladder
(A) affects the person’s health
(B) Has no effect on the person’s health
(C) Effects the secretion of bile
(D) Effects the digestion of proteins
Answer:
(B) Has no effect on the person’s health
Explanation:
No, the removal of gall bladder will not affect person’s health.

Question 3.
Which of the following statement is correct about bile?
(A) It helps in emulsification of fat.
(B) It helps in digestion of carbohydrates
(C) It helps in absorption of digested food.
(D) It helps in egestion of undigested food.
Answer:
(A) It helps in emulsification of fat.
Explanation:
Bile helps in emulsification of fat.
Question 4.
Which part of alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(A) Stomach
(B) Small intestine
(C) Large intestine
(D) Oesophagus
Answer:
(B) Small intestine
Explanation:
Bile is dark green or a yellowish brown fluid which is produced by the liver and comes to the small intestine through hepato-pancreatic duct.
Question 5.
What is the function of bile salt in the intestine?
(A) Activator of lipase
(B) Emulsifier
(C) Co factor of cholesteryl esterase
(D) Inhibitor of lipid absorption
Answer:
(B) Emulsifier
Explanation:
Bile contains bile salts that help in proper digestion of fats by breaking down large fat globules into smaller ones, so that enzyme can easily act on it and digest them. This process is known as emulsification of fats.
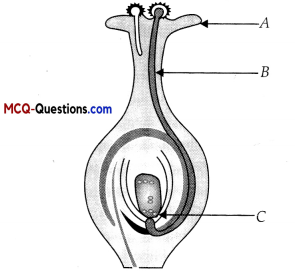
II. The given diagram is of human digestive human. Study the diagram and answer any of the four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.

Question 1.
Which of these correctly represent the labels B, C, D and E?
(A) B- Oesophagus, C- Liver, D- Stomach, E- pancreas
(B) B- Pancreas, C- Oesophagus, D- Liver, E- Stomach
(C) B- Stomach, C- Pancreas, D- Oesophagus, E- Liver
(D) B- Liver, C- Stomach, D- Pancreas, E- Oesophagus
Answer:
(A) B- Oesophagus, C- Liver, D- Stomach, E- pancreas
Explanation:
In the given picture of human digestive system, B is Oesophagus, C is Liver,D is Stomach, and E is pancreas.
Question 2.
The secretion that is released by label C is:
(A) Bile
(B) Pepsin
(C) Saliva
(D) Gastric juice
Answer:
(A) Bile
Explanation:
Label C represents liver. Liver secretes bile, which is stored in gall bladder.
Question 3.
Name the digestive juice that lacks enzyme but helps in digestion.
(A) Bile juice
(B) Pancreatic juice
(C) Ptyalin
(D) Pepsin
Answer:
(A) Bile juice
Explanation:
Bile juice doesn’t contain any enzyme. It helps in digestion of fats.
Question 4.
The digestion of food starts in
(A) A
(B) D
(C) E
(D) F
Answer:
(A) A
Explanation:
Label A represents mouth. The digestion of food starts in mouth.

Question 5.
In case of diarrhoea, which major process does not takes place normally in region F?
(A) Absorption of food
(B) Absorption of water
(C) Secretion of hormones
(D) Removal of waste material
Answer:
(B) Absorption of water
Explanation:
Absorption of water is not occurring normally in region F (Large I intestine).
III. Study the given flow chart and answer any of the four questions from Question l. to Question 5.
CO2+ H2OCO2+ C2H5OH +energy + energy

Question 1.
Identify X, Y and Z.
(A) X-Glycolysis, Y-Anaerobic, Z-Aerobic
(B) X -Krebs’s cycle, Y-Aerobic, Z-Anaerobic
(C) X-Glycolysis, Y-Aerobic, Z-Anaerobic
(D) X-Glycolysis, Y-Aerobic, Z-Krebs’s cycle
Answer:
(C) X-Glycolysis, Y-Aerobic, Z-Anaerobic
Explanation:
The label X represents the process of Glycolysis, Y – Aerobic respiration, and Z – Anaerobic respiration.
Question 2.
The process X occurs in……….. and Y occurs in………. part of cell.
(A) Mitochondria and cytoplasm respectively
(B) Cytoplasm and mitochondria respectively
(C) Both takes place in cytoplasm
(D) Both takes place in mitochondria
Answer:
(B) Cytoplasm and mitochondria respectively
Explanation:
The breakdown of glucose (a six- carbon molecule) into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate takes place in the cytoplasm whereas the process of aerobic respiration takes place in mitochondria.
Question 3.
In which of these organisms the process Z takes place?
(A) Bacteria
(B) Humans
(C) Yeast
(D) Spirogyra
Answer:
(C) Yeast
Explanation:
The Z (anaerobic respiration) takes place in yeast. Since the process takes place in the absence of air, it is called anaerobic respiration.
Question 4.
In which part of human body do the process Z takes place?
(A) In muscle cells
(B) In kidneys
(C) In liver cells
(D) In leydig’s cell
Answer:
(A) In muscle cells
Explanation:
In human body, Z (anaerobic respiration) takes place in muscle cells.

Question 5.
Where does aerobic respiration occur in a cell ?
(A) Mitochondria
(B) Cytoplasm
(C) Nucleus
(D) Plastid
Answer:
(A) Mitochondria
Explanation:
Aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria. Since the process takes place in presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration.
IV. Study the diagram of human respiratory system and answer any of the four questions Question 1. to Question 5.

Question 1.
The balloon like structures present in ‘S’ is:
(A) Nephron
(B) Alveoli
(C) Bronchi
(D) Bronchiole
Answer:
(C) Bronchi
Explanation:
The balloon like structure are alveoli. Alveoli are air sacs at the end of bronchioles. They allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to move between the lungs and the blood-stream.
Question 2.
Which of these organ is surrounded by cartilaginous rings?
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Answer:
(C) R
Explanation:
R (Trachea) is supported by rings I of cartilage.
Question 3.
Which of these statements is incorrect regarding human lungs?
(A)It is the secondary organ for respiration.
(B) It is located on the two sides of heart.
(C) The membrane that encloses lungs is pleural membrane.
(D) The alveolar epithelium of lungs is non-ciliated epithelium.
Answer:
(A)It is the secondary organ for respiration.
Explanation:
Lungs are the primary breathing organ. It is the main respiratory surface available for the exchange of gases (O2 CO2).

Question 4.
Trachea is divided into two smaller tubes called………… .
(A) Bronchi
(B) Bronchioles
(C) Larynx
(D) Alveoli
Answer:
(A) Bronchi
Explanation:
Pharynx splits into trachea and oesophagus. It connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs. It provides air flow to and from the lungs for respiration.
Question 5.
Which of these is the function of balloon like structure present in lungs?
(A) Exchange of gases
(B) Absorption of nutrients
(C) Transport of food
(D) Removal of waste materials
Answer:
(A) Exchange of gases
Explanation:
The balloon like structure called alveoli allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to move between the lungs and the blood-stream.
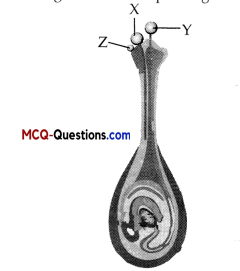
V. The given diagram represents the structure of a human excretory system. Study the diagram and answer any of the four questions from Question 1. to Question 5.

Question 1.
Identify the part in excretion.
(A) Kidney
(B) Ureter
(C) Urethra
(D) Nephron
Answer:
(B) Ureter
Explanation:
Part is ureter. It transports urine from kidney to urinary bladder.

Question 2.
Which of these is the structural and functional unit of part 2?
(A) Alveoli
(B) Nephron
(C) Neuron
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Nephron
Explanation:
Nephrons are the structural and functional filtration unit of kidney that serve in filtration, reabsorption and secretion.
Question 3.
How can we purify the blood by artificial methods?
(A) Filtration
(B) Dialysis
(C) Reabsorption
(D) All of these
Answer:
(B) Dialysis
Explanation:
Urea is the main waste present in the urine.
Question 4.
The main waste present in the urine is:
(A) Glucose
(B) Urea
(C) Blood
(D) Protein
Answer:
(B) Urea
Explanation:
Dialysis is a procedure to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys stop working properly. It often involves diverting blood to a machine to be cleaned.
Question 5.
Choose the correct path of urine in our body:
(A) kidney →tureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(B) kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(C) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
(D) urinary bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Answer:
(C) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
Explanation:
Kidneys are the paired organs where urine formation takes place. Small muscular tube, called as ureter, extend from kidneys and carries urine to urinary bladder. The urethra is a small tube that extends from the urinary bladder to an external opening.
VI. Read the given passage and answer any of the four questions from Question l. to Question 5.
Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs comes to the thin-walled upper chamber of the heart on the left. The left upper chamber (A) then relaxes. It then contracts and the blood is allowed to enter the next chamber (B), as it expands. When the muscular left lower chamber of heart contracts the blood is pumped out to the body via aorta.
Deoxygenated blood reaches from the body to the upper chamber on the right side of heart (C) and it expands. As this part contracts, the corresponding lower chamber (D) dilates. This transfers the blood to right ventricle, which in turn pumps it to the lungs for oxygenated.

Question 1.
Which of these correctly represents the label A, B, C and D in the above passage?
(A) A- Left atrium, B- Left Ventricle, C- Right atrium, D- Right ventricle
(B) A- Right ventricle, B- Left atrium, C- Left Ventricle, D- Right atrium
(C) A- Right atrium, B- Right ventricle, C- Left atrium, D- Left ventricle
(D) A- Left ventricle, B- Right atrium, C- Right ventricle, D- Left atrium
Answer:
(A) A- Left atrium, B- Left Ventricle, C- Right atrium, D- Right ventricle
Explanation:
A is Left atrium, B is Left Ventricle, C is Right atrium, and D is Right ventricle.
Question 2.
Which chambers of human heart contain oxygenated blood?
(A) A and B
(B) A and C
(C) C and B
(D) C and D
Answer:
(A) A and B
Explanation:
A (Left atrium) and B (Left ventricle) contain oxygenated blood from lungs.
Question 3.
What is the correct route of blood in a human?
(A) A → B → Lungs → C → D
(B) A → B → D → C → Lungs
(C) C → D → B→ A → Lungs
(D) C → D → Lung → A → B
Answer:
(D) C → D → Lung → A → B
Explanation:
The correct route of blood in a human is : C (Right atrium)→ D (Right ventricle) →Lungs → A (Left atrium) → B (Left ventricle.
Question 4.
What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(A) Valves in heart
(B) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(C) Thin walls of atria
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(A) Valves in heart
Explanation:
Valves prevent the back flow of blood inside the heart during contraction of heart chambers (atria or ventricles).
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Human heart does not allow mixing of oxygen rich blood with carbon dioxide rich blood.
Reason (R): Human heart has different chambers.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation:
Human heart is four chambered. It is composed of four chambers : right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle and left atrium. The chambers are separated by a muscular wall that prevents the mixing of the blood rich in oxygen with the blood rich in carbon dioxide.

VII. Read the passage and answer any of the four questions from Question l. to Question 5.
Some experiments were carried out using Croton sp. plants to understand the process of photosynthesis. It was observed that the leaves of the plant exposed to light for longer duration accumulated more starch. However, due to presence of pre-formed starch in the leaves, it was difficult to find the net productivity on a fixed exposure to light source. Therefore, it was necessary to obtain starch free leaves in the plant before starting the experiment.
Question 1.
Which of the following would help obtain starch free leaves in the plant?
(A) Expose the leaves to blue light for 48 hours before starting the experiment.
(B) Keep the plant in dark for about 48 hours before starting the experiment.
(C) Remove starch from the leaves by exosmosis, 48 hours before starting the experiment.
(D) Keep the leaves to red light for 48 hours before starting the experiment.
Answer:
(B) Keep the plant in dark for about 48 hours before starting the experiment.
Explanation:
The starch free leaves can be j obtained by keeping the plant in dark, so that 1 already present starch is utilized in 48 hrs.
Question 2.
After a period of illumination, the leaves were boiled in alcohol to make them colourless. Which of the following could be used to test the end product stored in the leaves?
(A) Cobalt chloride paper
(B) Litmus paper
(C) Iodine solution
(D) Copper sulphate solution
Answer:
(C) Iodine solution
Explanation:
Starch presence can be tested by adding iodine solution which gives bluish black colour of starch iodine mixture.
Question 3.
Some of the starch free leaves were coated with wax on both the surfaces. The plant was maintained under normal environmental conditions. At the end of the experiment, the wax coated leaves are likely to show .
(A) Accumulation of more water.
(B) Wilting of the wax coated leaves.
(C) Increase in sucrose accumulation.
(D) Decrease in number of chloroplasts
Answer:
(B) Wilting of the wax coated leaves.
Explanation:
Wilting occurs due to wax blocks the transpiration so water transportation inhibits.

Question 4.
During the morning hours, using a fine blade, an incision was made to the leaves such that the phloem tissue was cut open. Analysis of the liquid oozing out was found to contain high amount of:
(A) Xylose
(B) Ribose
(C) Sucrose
(D) Galactose
Answer:
(C) Sucrose
Explanation:
The transport of glucose, occurs in the form of sucrose, in phloem therefore, when cell sap oozes out, liquid contains sucrose.
Question 5.
The equation given below represents photosynthesis. Identify P and Question

(A) P – Carbon dioxide, Q – Oxygen
(B) P – Oxygen, Q – Oxygen
(C) P – Carbon dioxide, Q – Carbon dioxide
(D) P – Oxygen, Q – Carbon dioxide
Answer:
(A) P – Carbon dioxide, Q – Oxygen
Explanation:
The process by which autotrophs take in CO2 and H2 O and convert these into carbohydrates in the presence of chlorophyll, and sunlight is called photosynthesis.
Equation for photosynthesis is :

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()